Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2017-2018
Date: March 2018
Advertisements
Write the IUPAC name of the following :
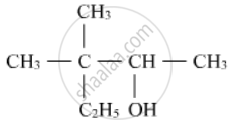
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Out of chlorobenzene and benzyl chloride, which one gets easily hydrolysed by aqueous NaOH and why?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
CO (g) and H2 (g) react to give different products in the presence of different catalysts. Which ability of the catalyst is shown by these reactions?
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Write the coordination number and oxidation state of Platinum in the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2].
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
An analysis shows that FeO has a non-stoichiometric composition with formula Fe0.95O. Give reason.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Complete and balance the following chemical equations
`Fe^(2+) + MnO_4^(-) + H^+ ->`
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Complete and balance the following chemical equations
`MnO_4^(-) + H_2O + I^(-) ->`
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
How do you convert the Ethanal to Propanone
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
How do you convert the Toluene to Benzoic acid
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Account for the following:
Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Account for the following:
pKa value of 4-nitrobenzoic acid is lower than that of benzoic acid.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
For the reaction
2N2O5 (g) → 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g), the rate of formation of NO2 (g) is 2·8 × 10–3 M s–1. Calculate the rate of disappearance of N2O5 (g).
Chapter:
Among the hydrides of Group-15 elements, which have the lowest boiling point?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Among the hydrides of Group-15 elements, which have the maximum basic character?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Among the hydrides of Group-15 elements, which have the highest bond angle?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Among the hydrides of Group-15 elements, which have the maximum reducing character?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Calculate the freezing point of a solution containing 60 g of glucose (Molar mass = 180 g mol–1) in 250 g of water. (Kf of water = 1.86 K kg mol–1)
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Advertisements
An element 'X' (At. mass = 40 g mol-1) having f.c.c. the structure has unit cell edge length of 400 pm. Calculate the density of 'X' and the number of unit cells in 4 g of 'X'. (NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol-1)
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Give reasons for the following:
Measurement of osmotic pressure method is preferred for the determination of molar masses of macromolecules such as proteins and polymers.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Give reasons for the following :
Aquatic animals are more comfortable in the cold water than in warm water.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Give reasons for the following
Elevation of the boiling point of 1 M KCl solution is nearly double than that of 1 M sugar solution.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Write the structures of the main products in the following reactions :
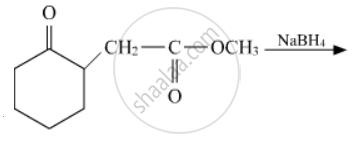
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write the structures of the main products in the following reactions :
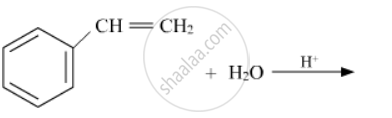
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Write the structures of the main products in the following reactions :
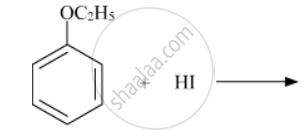
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the formula for the given coordination compound:
Iron (III) hexacyanoferrate (II)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
What type of isomerism is exhibited by the complex `[Co(NH_3)_5Cl]SO_4`?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons in the complex `[CoF_6]^(3-)`. (Atomic No. of Co = 27)
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
(A), (B) and (C) are three non-cyclic functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C4H8O. Isomers (A) and (C) give positive Tollens' test whereas isomer (B) does not give Tollens' test but gives positive Iodoform test. Isomers (A) and (B) on reduction with Zn(Hg)/conc. HCl give the same product (D).
1) Write the structures of (A), (B), (C) and (D).
2) Out of (A), (B), and (C) isomers, which one is least reactive towards the addition of HCN?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Identify the chiral molecule in the following pair :
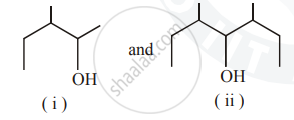
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the structure of the product when chlorobenzene is treated with methyl chloride in the presence of sodium metal and dry ether.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Write the structure of the alkene formed by dehydrohalogenation of 1-Bromo-1methylcyclohexane with alcoholic KOH.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Give reasons: E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Fe3+/Fe2+.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Give reasons Iron has the higher enthalpy of atomization than that of copper.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Give reasons: Sc3+ is colourless in aqueous solution whereas Ti3+ is coloured.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Write the chemical reactions involved in the process of extraction of Gold. Explain the role of dilute NaCN and Zn in this process.
Chapter: [0.06] General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Define the following with an example of each
Polysaccharides
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Define the following with an example
Denatured protein
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Define the following terms: Essential amino acids
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Write the product when D-glucose reacts with conc. HNO3.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Amino acids show amphoteric behaviour. Why?
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Write one difference between α-helix and β-pleated structures of proteins.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
A first-order reaction is 50% completed in 40 minutes at 300 K and in 20 minutes at 320 K. Calculate the activation energy of the reaction. (Given : log 2 = 0·3010, log 4 = 0·6021, R = 8·314 JK–1 mol–1)
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Advertisements
Why is bithional added to soap?
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
What is tincture of iodine? What is its use?
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
Among the following, which one acts as a food preservative?
Aspartame, Aspirin, Sodium Benzoate, Paracetamol
Chapter: [0.16] Chemistry in Everyday Life
What happens when a freshly prepared precipitate of Fe(OH)3 is shaken with a small amount of FeCl3 solution?
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
What happens when persistent dialysis of a colloidal solution is carried out?
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
What happens when an emulsion is centrifuged?
Chapter: [0.05] Surface Chemistry
Shyam went to a grocery shop to purchase some food items. The shopkeeper packed all the items in polythene bags and gave them to Shyam. But Shyam refused to accept the polythene bags and asked the shopkeeper to pack the items in paper bags. He informed the shopkeeper about the heavy penalty imposed by the government for using polythene bags. The shopkeeper promised that he would use paper bags in future in place of polythene bags.
1) Write the values (at least two) shown by Shyam.
2) Write one structural difference between low-density polyethene and high-density polyethene.
3) Why did Shyam refuse to accept the items in polythene bags?
4) What is a biodegradable polymer? Give an example.
Chapter: [0.15] Polymers
Write the cell reaction and calculate the e.m.f of the following cell at 298 K:
`Sn(s) | Sn^(2+) (0.004 M) || H^(+) (0.020 M) | H_2 (g) ("1 bar") | Pt(s)`
(Given: `E_(Sn^(2+)"/"Sn)^0 = -0.14` V)
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Give reasons On the basis of E° values, O2 gas should be liberated at anode but it is Cl2 gas which is liberated in the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Give reasons Conductivity of CH3COOH decreases on dilution.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
For the reaction
`2AgCl (s) + H_2 (g) ("1 atm") -> 2Ag (s) + 2H^(+) (0.1 M) + 2Cl^(-) (0.1 M)`
`triangleG^0 = -43600 J at 25^@ C`
Calculate the e.m.f. of the cell
`[log 10^(-n) = -n]`
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Define terms: Fuel cell
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Write two advantages of fuel cell
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Write the chemical equation involved in the following reaction:
Hoffmann-bromamide degradation reaction
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Illustrate the following reaction giving suitable example in each case: Diazotisation
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Illustrate the following reaction giving suitable example in each case:Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reason (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reason Aromatic diazonium salts are more stable than aliphatic diazonium salts.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the structures of the main products of the following reactions:
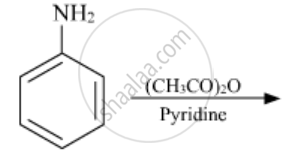
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the structures of the main products of the following reactions:

Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the structures of the main products of the following reactions:
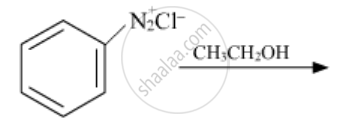
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between Aniline and N, N-dimethylaniline
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their pKb values:
C6H5NH2, C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons H3PO3 undergoes disproportionation reaction but H3PO4 does not.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Give reasons When Cl2 reacts with the excess of F2, ClF3 is formed and not FCl3.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Give reasons Dioxygen is a gas while Sulphur is a solid at room temperature.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Draw the structures of the following molecules: XeF4
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Draw the structures of the HClO3.
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
When concentrated sulphuric acid was added to an unknown salt present in a test tube a brown gas (A) was evolved. This gas intensified when copper turnings were added to this test tube. On cooling, the gas (A) changed into a colourless solid (B).
1) Identify (A) and (B).
2) Write the structures of (A) and (B).
3) Why does gas (A) change to solid on cooling?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Arrange the following in the decreasing order of their reducing character :
HF, HCl, HBr, HI
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
What happens when: XeF4 reacts with SbF5?
Chapter: [0.07] P - Block Elements
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2017 - 2018
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2018 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
