Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
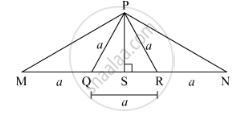
From the information given in the figure, prove that PM = PN = \[\sqrt{3}\] × a
Solution 1
Since ∆PQR is an equilateral triangle, PS is the perpendicular bisector of QR.
∴ QS = SR = \[\frac{a}{2}\] ...(1)
Now, According to Pythagoras theorem,
In ∆PQS,
\[{PQ}^2 = {QS}^2 + {PS}^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow a^2 = \left( \frac{a}{2} \right)^2 + {PS}^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow {PS}^2 = a^2 - \frac{a^2}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {PS}^2 = \frac{4 a^2 - a^2}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {PS}^2 = \frac{3 a^2}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow PS = \frac{\sqrt{3}a}{2} . . . \left( 2 \right)\]
In ∆PMS,
\[ \Rightarrow {PM}^2 = \left( a + \frac{a}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a \right)^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow {PM}^2 = \left( \frac{3a}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a \right)^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow {PM}^2 = \frac{9 a^2}{4} + \frac{3 a^2}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {PM}^2 = \frac{12 a^2}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {PM}^2 = 3 a^2 \] ...Taking square root
\[ \Rightarrow PM = \sqrt{3}a . . . \left( 3 \right)\]
In ∆PNS,
\[{PN}^2 = {NS}^2 + {PS}^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow {PN}^2 = \left( a + \frac{a}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a \right)^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow {PN}^2 = \left( \frac{3a}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a \right)^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow {PN}^2 = \frac{9 a^2}{4} + \frac{3 a^2}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {PN}^2 = \frac{12 a^2}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {PN}^2 = 3 a^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow PN = \sqrt{3}a . . . \left( 4 \right)\]
From (3) and (4), we get
PM = PN =\[\sqrt{3}\] × a
Hence, PM = PN =\[\sqrt{3}\]× a.
Solution 2
From figure,
In ∆PMR
MQ = QR = a ...(given)
∴ Q is a midpoint of MR.
∴ seg PQ is the median.
∴ According to Apollonius's theorem,
PM2 + PR2 = 2PQ2 + 2MQ2
∴ PM2 + a2 = 2a2 + 2a2
∴ PM2 + a2 = 4a2
∴ PM2 = 4a2 − a2
∴ PM2 = 3a2 ...Taking square root
PM = `sqrt3 xx a` ....(i)
From figure,
In ∆PNQ
NR = RQ = a ...(given)
∴ R is a midpoint of NQ.
∴ seg PR is the median.
∴ According to Apollonius's theorem,
PN2 + PQ2 = 2PR2 + 2NR2
∴ PN2 + a2 = 2a2 + 2a2
∴ PN2 + a2 = 4a2
∴ PN2 = 4a2 − a2
∴ PN = 3a2 ...Taking square root
PN = `sqrt3 xx a` ....(ii)
From (3) and (4), we get
PM = PN =\[\sqrt{3}\] × a
∴ PM = PN =\[\sqrt{3}\]× a.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
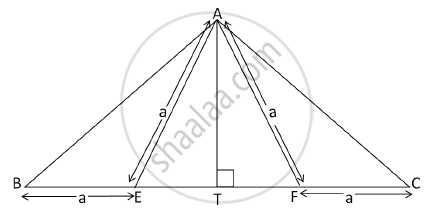
In the following figure, AE = EF = AF = BE = CF = a, AT ⊥ BC. Show that AB = AC = `sqrt3xxa`
Find the length of the side and perimeter of an equilateral triangle whose height is `sqrt3` cm.
∆ABC is an equilateral triangle. Point P is on base BC such that PC = `1/3`BC, if AB = 6 cm find AP.
Find the length of the hypotenuse in a right angled triangle where the sum
of the squares of the sides making right angle is 169.
(A)15 (B) 13 (C) 5 (D) 12
Prove that, in a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is
equal to the sum of the squares of remaining two sides.
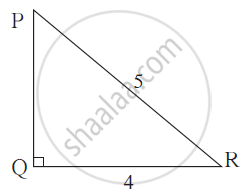
In right angled triangle PQR,
if ∠ Q = 90°, PR = 5,
QR = 4 then find PQ and hence find tan R.
Choose the correct alternative:
ΔABC and ΔDEF are equilateral triangles. If ar(ΔABC): ar(ΔDEF) = 1 : 2 and AB = 4, then what is the length of DE?
From given figure, In ∆ABC, AD ⊥ BC, then prove that AB2 + CD2 = BD2 + AC2 by completing activity.
Activity: From given figure, In ∆ACD, By pythagoras theorem
AC2 = AD2 + `square`
∴ AD2 = AC2 – CD2 ......(I)
Also, In ∆ABD, by pythagoras theorem,
AB2 = `square` + BD2
∴ AD2 = AB2 – BD2 ......(II)
∴ `square` − BD2 = AC2 − `square`
∴ AB2 + CD2 = AC2+ BD2
A ladder 10 m long reaches a window 8 m above the ground. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the base of wall. Complete the given activity.
Activity: As shown in figure suppose

PR is the length of ladder = 10 m
At P – window, At Q – base of wall, At R – foot of ladder
∴ PQ = 8 m
∴ QR = ?
In ∆PQR, m∠PQR = 90°
By Pythagoras Theorem,
∴ PQ2 + `square` = PR2 .....(I)
Here, PR = 10, PQ = `square`
From equation (I)
82 + QR2 = 102
QR2 = 102 – 82
QR2 = 100 – 64
QR2 = `square`
QR = 6
∴ The distance of foot of the ladder from the base of wall is 6 m.
Complete the following activity to find the length of hypotenuse of right angled triangle, if sides of right angle are 9 cm and 12 cm.
Activity: In ∆PQR, m∠PQR = 90°
By Pythagoras Theorem,
PQ2 + `square` = PR2 ......(I)
∴ PR2 = 92 + 122
∴ PR2 = `square` + 144
∴ PR2 = `square`
∴ PR = 15
∴ Length of hypotenuse of triangle PQR is `square` cm.
From given figure, in ∆PQR, if ∠QPR = 90°, PM ⊥ QR, PM = 10, QM = 8, then for finding the value of QR, complete the following activity.

Activity: In ∆PQR, if ∠QPR = 90°, PM ⊥ QR, ......[Given]
In ∆PMQ, by Pythagoras Theorem,
∴ PM2 + `square` = PQ2 ......(I)
∴ PQ2 = 102 + 82
∴ PQ2 = `square` + 64
∴ PQ2 = `square`
∴ PQ = `sqrt(164)`
Here, ∆QPR ~ ∆QMP ~ ∆PMR
∴ ∆QMP ~ ∆PMR
∴ `"PM"/"RM" = "QM"/"PM"`
∴ PM2 = RM × QM
∴ 102 = RM × 8
RM = `100/8 = square`
And,
QR = QM + MR
QR = `square` + `25/2 = 41/2`
Find the diagonal of a rectangle whose length is 16 cm and area is 192 sq.cm. Complete the following activity.
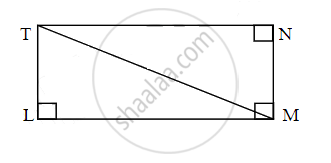
Activity: As shown in figure LMNT is a reactangle.
∴ Area of rectangle = length × breadth
∴ Area of rectangle = `square` × breadth
∴ 192 = `square` × breadth
∴ Breadth = 12 cm
Also,
∠TLM = 90° ......[Each angle of reactangle is right angle]
In ∆TLM,
By Pythagoras theorem
∴ TM2 = TL2 + `square`
∴ TM2 = 122 + `square`
∴ TM2 = 144 + `square`
∴ TM2 = 400
∴ TM = 20
A congruent side of an isosceles right angled triangle is 7 cm, Find its perimeter
ΔPQR, is a right angled triangle with ∠Q = 90°, QR = b, and A(ΔPQR) = a. If QN ⊥ PR, then prove that QN = `(2ab)/sqrt(b^4 + 4a^2)`
