Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
▶ 2: Pythagoras Theorem
3: Circle
4: Geometric Constructions
5: Co-ordinate Geometry
6: Trigonometry
7: Mensuration
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 2: Pythagoras Theorem
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2 of Maharashtra State Board Balbharati for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board.
Balbharati solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 2 Pythagoras Theorem Practice Set 2.1 [Pages 38 - 39]
Identify, with reason, if the following is a Pythagorean triplet.
(3, 5, 4)
Identify, with reason, if the following is a Pythagorean triplet.
(4, 9, 12)
Identify, with reason, if the following is a Pythagorean triplet.
(5, 12, 13)
Identify, with reason, if the following is a Pythagorean triplet.
(24, 70, 74)
Identify, with reason, if the following is a Pythagorean triplet.
(10, 24, 27)
Identify, with reason, if the following is a Pythagorean triplet.
(11, 60, 61)
In the given figure, ∠MNP = 90°, seg NQ ⊥ seg MP, MQ = 9, QP = 4, find NQ.
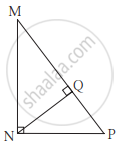
In the given figure, ∠QPR = 90°, seg PM ⊥ seg QR and Q–M–R, PM = 10, QM = 8, find QR.

In the given figure. Find RP and PS using the information given in ∆PSR.

For finding AB and BC with the help of information given in the figure, complete following activity.
AB = BC .......... 
∴ ∠BAC = 
∴ AB = BC =  × AC
× AC
=  × `sqrt8`
× `sqrt8`
=  × `2sqrt2`
× `2sqrt2`
= 

Find the side and perimeter of a square whose diagonal is 10 cm.
In the given figure, ∠DFE = 90°, FG ⊥ ED, If GD = 8, FG = 12, find (1) EG (2) FD and (3) EF

Find the length diagonal of a rectangle whose length is 35 cm and breadth is 12 cm.
In the given figure, M is the midpoint of QR. ∠PRQ = 90°. Prove that, PQ2 = 4PM2 – 3PR2.
Walls of two buildings on either side of a street are parallel to each other. A ladder 5.8 m long is placed on the street such that its top just reaches the window of a building at the height of 4 m. On turning the ladder over to the other side of the street, its top touches the window of the other building at a height 4.2 m. Find the width of the street.
Balbharati solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 2 Pythagoras Theorem Practice Set 2.2 [Page 43]
In ∆PQR, point S is the midpoint of side QR. If PQ = 11, PR = 17, PS = 13, find QR.
In ∆ABC, AB = 10, AC = 7, BC = 9, then find the length of the median drawn from point C to side AB.
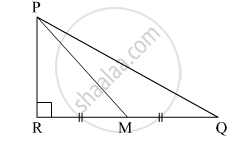
In the given figure, seg PS is the median of ∆PQR and PT ⊥ QR. Prove that,
PR2 = PS2 + QR × ST + `("QR"/2)^2`
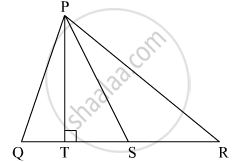
In the given figure, seg PS is the median of ∆PQR and PT ⊥ QR. Prove that,
PQ2 = PS2 − QR × ST + `(("QR")/2)^2`

In ∆ABC, point M is the midpoint of side BC. If, AB2 + AC2 = 290 cm2, AM = 8 cm, find BC.

In the given figure, point T is in the interior of rectangle PQRS, Prove that, TS2 + TQ2 = TP2 + TR2 (As shown in the figure, draw seg AB || side SR and A-T-B)

Balbharati solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 2 Pythagoras Theorem Problem Set 2 [Pages 43 - 46]
Out of the following, which is the Pythagorean triplet?
(1, 5, 10)
(3, 4, 5)
(2, 2, 2)
(5, 5, 2)
Some question and their alternative answer are given.
In a right-angled triangle, if sum of the squares of the sides making right angle is 169 then what is the length of the hypotenuse?
15
13
5
12
Four alternative answers for the following question are given. Choose the correct alternative and write its alphabet:
Out of the dates given below which date constitutes a Pythagorean triplet?
15/8/17
16/8/16
3/5/17
4/9/15
Some question and their alternative answer are given. Select the correct alternative.
If a, b, and c are sides of a triangle and a2 + b2 = c2, name the type of triangle.
Obtuse angled triangle
Acute angled triangle
Right-angled triangle
Equilateral triangle
Some question and their alternative answer are given. Select the correct alternative.
Find perimeter of a square if its diagonal is \[10\sqrt{2}\]
10 cm
\[40\sqrt{2}\]cm
20 cm
40 cm
Some question and their alternative answer are given. Select the correct alternative.
Altitude on the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle divides it in two parts of lengths 4 cm and 9 cm. Find the length of the altitude.
9 cm
4 cm
6 cm
\[2\sqrt{6}\] cm
Height and base of a right angled triangle are 24 cm and 18 cm find the length of its hypotenuse
24 cm
30 cm
15 cm
18 cm
Some question and their alternative answer are given. Select the correct alternative.
In ∆ABC, AB = \[6\sqrt{3}\] cm, AC = 12 cm, BC = 6 cm. Find measure of ∠A.
30°
60°
90°
45°
Solve the following examples.
Find the height of an equilateral triangle having side 2a.
Do sides 7 cm, 24 cm, 25 cm form a right angled triangle ? Give reason
Find the length a diagonal of a rectangle having sides 11 cm and 60 cm.
Find the length of the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle if remaining sides are 9 cm and 12 cm.
A side of an isosceles right angled triangle is x. Find its hypotenuse.
In ∆PQR, PQ = √8 , QR = √5 , PR = √3. Is ∆PQR a right-angled triangle? If yes, which angle is of 90°?
In ∆RST, ∠S = 90°, ∠T = 30°, RT = 12 cm then find RS and ST.
Find the diagonal of a rectangle whose length is 16 cm and area is 192 sq.cm ?
Find the length of the side and perimeter of an equilateral triangle whose height is `sqrt3` cm.
In ∆ABC, seg AP is a median. If BC = 18, AB2 + AC2 = 260, Find AP.
∆ABC is an equilateral triangle. Point P is on base BC such that PC = `1/3`BC, if AB = 6 cm find AP.
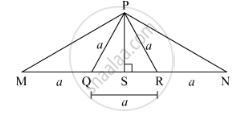
From the information given in the figure, prove that PM = PN = \[\sqrt{3}\] × a
Prove that the sum of the squares of the diagonals of a parallelogram is equal to the sum of the squares of its sides.
Pranali and Prasad started walking to the East and to the North respectively, from the same point and at the same speed. After 2 hours distance between them was \[15\sqrt{2}\]
km. Find their speed per hour.
In ∆ABC, ∠BAC = 90°, seg BL and seg CM are medians of ∆ABC. Then prove that:
4(BL2 + CM2) = 5 BC2
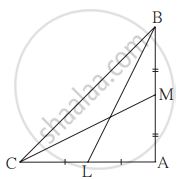
Sum of the squares of adjacent sides of a parallelogram is 130 sq.cm and length of one of its diagonals is 14 cm. Find the length of the other diagonal.
In ∆ABC, seg AD ⊥ seg BC, DB = 3CD.
Prove that: 2AB2 = 2AC2 + BC2
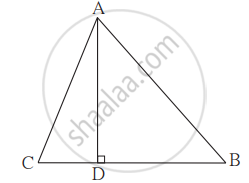
In an isosceles triangle, length of the congruent sides is 13 cm and its base is 10 cm. Find the distance between the vertex opposite the base and the centroid.
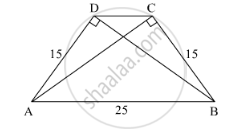
In a trapezium ABCD, seg AB || seg DC seg BD ⊥ seg AD, seg AC ⊥ seg BC, If AD = 15, BC = 15 and AB = 25. Find A(▢ABCD)
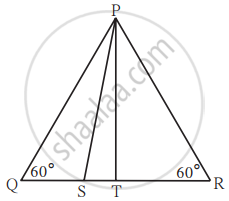
In the given figure, ∆PQR is an equilateral triangle. Point S is on seg QR such that QS = n\[\frac{1}{3}\] QR.
Prove that: 9 PS2 = 7 PQ2
Seg PM is a median of ∆PQR. If PQ = 40, PR = 42 and PM = 29, find QR.
Seg AM is a median of ∆ABC. If AB = 22, AC = 34, BC = 24, find AM
Solutions for 2: Pythagoras Theorem
Balbharati solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 2 - Pythagoras Theorem
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Balbharati solutions for Mathematics Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board 2 (Pythagoras Theorem) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Balbharati textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 2 Pythagoras Theorem are Similarity in Right Angled Triangles, Theorem of Geometric Mean, Converse of Pythagoras Theorem, Application of Pythagoras Theorem in Acute Angle and Obtuse Angle, Apollonius Theorem, Right-angled Triangles and Pythagoras Property, Pythagoras Theorem, Pythagorean Triplet, Property of 30°- 60°- 90° Triangle Theorem, Property of 45°- 45°- 90° Triangle Theorem.
Using Balbharati Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board solutions Pythagoras Theorem exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Balbharati Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board students prefer Balbharati Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2, Pythagoras Theorem Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board additional questions for Mathematics Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![Balbharati solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 2 - Pythagoras Theorem Balbharati solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board chapter 2 - Pythagoras Theorem - Shaalaa.com](/images/geometry-mathematics-2-english-10-standard-ssc-maharashtra-state-board_6:e2c9bb85175b46e28111cc27e179e2ce.png)
