Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
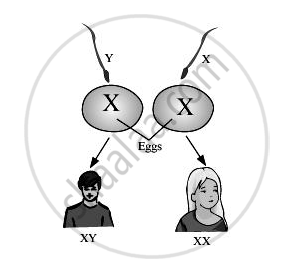
Gender of child is determined by the male partner of couple. Explain with reasons whether this statement is true or false.
Solution
Human females have two X chromosomes (XX) and human males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). Therefore, the eggs produced by females have only X chromosomes while the sperms produced by males can have either X or Y chromosome. If an unfertilised egg fuses with a sperm containing X chromosome, then it gives rise to a girl child having two X chromosomes. If an unfertilised egg fuses with a sperm containing Y chromosome, then it gives rise to a male child having one X and one Y chromosome.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the functions of the following organs of reproduction:
a. Ovaries
b. Seminal vesicle and prostate glands
Describe, in brief, the changes the uterus undergoes
(i) to receive the zygote.
(ii) if zygote is not formed
Write the functions of the following parts in human female reproductive system:-
(i) Ovary
(ii) Oviduct
(iii) Uterus
What are the functions of testes in the human male reproductive system?
What are sexually transmitted diseases?
Name the cells that secrete Testosterone
Give scientific reasons: When an ovum gets fertilized, menstrual cycle stops temporarily in a woman.
Give technical terms for Thin walled sac of skin which covers the testes
What are the female sex cells in humans called?
Write the names of male sex hormone?
Write the names of female sex hormones.
What name is given to the fusion of sperm and ovum?
What is the scientific name of womb?
Which structure in human female is equivalent to the penis in the male?and in what respect the structures are equivalent?
How long does a human baby take to develop before birth?
Draw a labelled diagram of the human male reproductive system. With the help of this diagram, describe the working of human male reproductive system?
Where does fertilisation take place in human females?
Which among the following are not the functions of testes at puberty?
(i) formation of germ cells
(ii) secretion of testosterone
(iii) development of the placenta
(iv) secretion of estrogen
The male gametes in a flower and in a human are produced respectively in :
(a) stigma and ovary
(b) anther and style
(c) ovary and testes
(d) anther and testes
When a female child is born, her ovaries already contain thousands of immature eggs (or ova) contained in immature structures A. On maturing, A bursts open and an egg shoots out of the ovary in a process called B. The process B starts in the females at puberty and occurs again and again after a time period x. Before every occurrence of process B, the inner lining of uterus becomes thick and soft with lots of blood vessels in it. When the egg cell gets fertilised by a sperm, then an event C occurs in the life of mature human female which lasts for time period y leading to the birth of baby. If, however, the egg cell released by the ovary does not get a sperm to fuse with, then the thick and soft inner lining of uterus breaks down and comes out of the female's body in an event called D. The occurrence of event D is controlled by chemical substances E.
(a) What are A?
(b) What is process B?
(c) What is the time period x?
(d) Name the event C.
(e) How much is the time period y?
(f) What is the name of process D?
(g) Name the chemical substances E.
Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the following parts :
(i) Where the development of egg occurs.
(ii) Where fertilization takes place.
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Oviducts and fallopian tubes are one and the same thing.
Give appropriate term of the following:
The onset of reproductive phase in a young female.
Choose the correct answer:
When pregnancy does not occur, the life of corpus luteum is about _____________
Name the following:
Male and Female organs on specific individuals.
Give the function of the following:
Uterus
Define the following:
Monoceious
Name the organs of the human male reproductive system and state the functions of any two organs.
The below diagram is of a developing embryo is a mother’s womb:

(i) Write the functions of the placenta, amnion, and umbilical cord.
(ii) How are the waste products of a fetus removed?
(iii) What is the gestation period?
The male homologue of the female clitoris is ____________.
Mention the importance of the position of the testes in humans.
What is the composition of semen?
The following is the illustration of the sequence of ovarian events (a-i) in a human female.
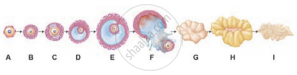
Write the difference between C and H.
The living organisms can be unexceptionally distinguished from the non-living things on the basis of their ability for ______.
Given below are the events in human reproduction. Write them in correct sequential order.
Insemination, gametogenesis, fertilisation, parturition, gestation, implantation
A zygote is formed by the fusion of a male gamete and a female gamete. The number of chromosomes in the zygote of a human is ______.
Given below is a group of terms. In the group, one pair indicates the relationship between the two terms. Rewrite and complete the second pair on a similar basis.
Female gonad : Ovaries :: Male gonad : ______.
