Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Give reasons:
The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
Explain why the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride?
Solution
- To understand the lower dipole moment of chlorobenzene, we must examine the contributing structures of the molecules.
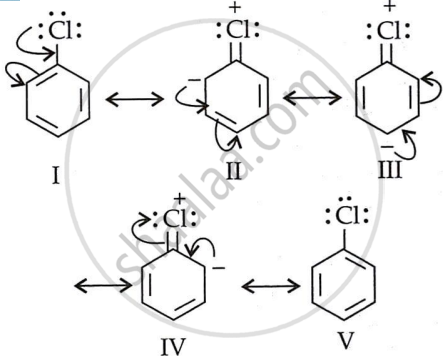
- The C-Cl bond in chlorobenzene has a partial double bond character (structures II, III, and IV). As a result, the C-Cl bond length is shorter than a single bond but longer than a double bond.
- The positive charge on the Cl atom minimizes the expected negative (δ−) charge due to electronegativity.
- As a result, the dipole moment is determined by bond length and partial negative charge on the Cl atom, decreases. However, this does not occur with cyclohexyl chloride. The carbon in this alkyl halide is purely sp3 hybridized, with a bond length of a single bond and a greater dipole moment due to the presence of (δ−) on Cl.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
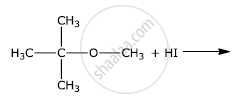
What happens when \[\ce{CH3 - Br}\] is treated with KCN?
Write the final product(s) in each of the following reactions:
The presence of nitro group (−NO2) at o/p positions increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Chlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol
Write chemical equation in support of your answer.
Out of  Cl and
Cl and  CH2- Cl, which one is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction and why?
CH2- Cl, which one is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction and why?
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 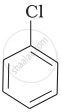 |
| (b) | 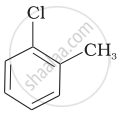 |
| (c) | 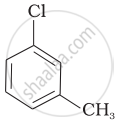 |
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 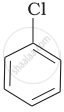 |
| (b) | 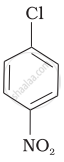 |
| (c) | 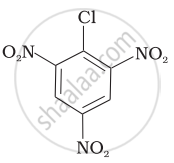 |
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 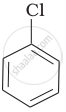 |
| (b) | 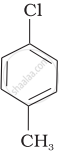 |
| (c) |  |
Assertion: Chlorobenzene is resistant to nucleophilic substitution reaction at room temperature.
Reason (R): C–Cl bond gets weaker due, to resonance.
Why haloarenes are not reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction? Give two reactions.
