Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give the main experimental points only to demonstrate that candle-gains weight on burning.
Solution
Candle gains weight on burning
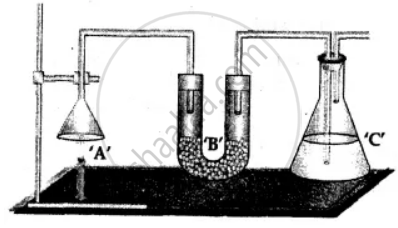
1. Weight: The complete apparatus as shown above which includes -
- Unlit candle ‘A’.
- U tube ‘B’ containing anhydrous CaCl2.
- Conical flask ‘C’ containing cone. KOH soln.
Total wt. = a gms.
The candle ‘A’ is then lit and the products obtained on burning are allowed to be absorbed in U tube ‘B’ and conical flask ‘C’.
2. Re-weigh: The complete apparatus as shown above after the candle has burnt – for a known period of time.
Total wt. = b gms.
Result:
- ‘b’ gms. is greater than ‘a’ gms.
- weight of apparatus after absorbtion
- of products is greater than the original weight of the apparatus.
Conclusion: Candle gains weight due to mass of oxygen of the air which has combined with ‘carbon’ and ‘hydrogen’ of the candle [CxHy] producing .
- Water vapour [absorbed by anhydrous CaCl2]
- Carbon dioxide [absorbed by cone. KOH soln].
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A metal highly resistant to rusting.
What do you observe when Magnesium is heated and then tested with moist blue and red litmus – paper?
Fill in the blanks :
Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen combine with rain water to form ___________ and _________ which cause ____________.
State and explain two ways by which air gets polluted in nature.
What happens when Iron burns in oxygen ? Also give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
Oxygen of the air is utilised for ‘combustiop’ and for ‘respiration’. Compare the two with a suitable examples.
Identify the acidic oxides responsible for acid rain. State how their presence results in formation of acid rain. Give a reason why acid rain damages heritage buildings.
In the laboratory preparation of oxygen from hydrogen peroxide answer the following:
State the method of collection of the oxygen gas giving reasons.
Name the following:
The pollutant which combines with water vapour to give sulphuric acid – a product of acid rain.
Name the following:
The gas required for both combustion and rusting.
