Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane?
Solution
Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the given three steps.
Step 1: Initiation:
The reaction begins with the homolytic cleavage of Cl – Cl bond as:
\[\ce{\underset{Chlorine free radicals}{Cl - Cl ->[hv]\overset\bullet{\text{Cl}} + \overset\bullet{\text{C}}}}\]
Step 2: Propagation:
In the second step, chlorine free radicals attack methane molecules and break down the C–H bond to generate methyl radicals as:
\[\ce{\underset{Methane}{CH4} + \overset\bullet{\text{Cl}} ->[hv] \overset\bullet{\text{C}}H3 + H - Cl}\]
These methyl radicals react with other chlorine free radicals to form methyl chloride along with the liberation of a chlorine free radical.
\[\ce{\overset\bullet{\text{C}}H3 + Cl - Cl -> \underset{Methyl chloride}{CH3 - Cl +}\overset\bullet{\text{C}}l}\]
Hence, methyl free radicals and chlorine free radicals set up a chain reaction. While HCl and CH3Cl are the major products formed, other higher halogenated compounds are also formed as:
\[\ce{CH3Cl + \overset\bullet{\text{C}}l -> \overset\bullet{\text{C}}H2Cl + HCl}\]
\[\ce{\overset\bullet{\text{C}}H2Cl + Cl - Cl -> CH2Cl2 + \overset\bullet{\text{C}}l}\]
Step 3: Termination:
Formation of ethane is a result of the termination of chain reactions taking place as a result of the consumption of reactants as:
\[\ce{\overset\bullet{\text{C}}l + \overset\bullet{\text{C}}l -> Cl - Cl}\]
\[\ce{H3\overset\bullet{\text{C}} + \overset\bullet{\text{C}}H3 -> \underset{(Ethane)}{H3C - CH3}}\]
Hence, by this process, ethane is obtained as a by-product of chlorination of methane.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Rotation around carbon-carbon single bond of ethane is not completely free. Justify the statement.
Draw Newman and Sawhorse projections for the eclipsed and staggered conformations of ethane. Which of these conformations is more stable and why?
Rotation of one conformer by an angle between 0° to 60° generates ______.
The dihedral angle between the hydrogen atoms of 2 methyl groups in staggered conformation of ethane is
The dihedral angle of the least stable conformer of ethane is ______.
How many conformations does ethane have?
Consider the following carbocations:
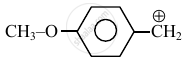
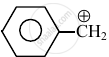
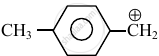
- \[\ce{CH3 - \overset{⊕}{CH2}}\]
The relative stabilities of these carbocations are such that:
