Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Structure of Atom
3: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
5: States of Matter
6: Thermodynamics
7: Equilibrium
8: Redox Reactions
9: Hydrogen
10: The s-Block Elements
11: The p-Block Elements
12: Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
▶ 13: Hydrocarbons
14: Environmental Chemistry
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 13: Hydrocarbons
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 13 of CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC NCERT for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11.
NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 13 Hydrocarbons EXERCISES [Pages 404 - 405]
How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane?
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
CH3CH = C(CH3)2
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
CH2 = CH - C ≡ C - CH3
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:

Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
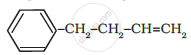
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:

Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3(CH2)4 CH(CH2)3 CH3}\\
|\phantom{..}\\
\phantom{..............}\ce{CH2 - CH(CH3)2}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH = CH - CH2 - CH = CH - CH - CH2 - CH = CH2}\\
\phantom{.................}|\\\phantom{.....................}\ce{C2H5}\end{array}\]
For the following compound, write structural formula and IUPAC name for all possible isomers having the number of a double or triple bond as indicated:
C4H8 (one double bond)
For the following compound, write structural formula and IUPAC name for all possible isomers having the number of the double or triple bond as indicated:
C5H8 (one triple bond)
Write IUPAC name of the product obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compound.
Pent-2-ene
Write IUPAC name of the product obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compound:
3,4-Dimethyl-hept-3-ene
Write IUPAC name of the product obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compound:
2-Ethylbut-1-ene
Write IUPAC name of the product obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compound:
1-Phenylbut-1-ene
An alkene ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Write structure and IUPAC name of ‘A’.
An alkene ‘A’ contains three C – C, eight C – H σ bonds and one C – C π bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u. Write IUPAC name of ‘A’.
Propanal and pentan-3-one are the ozonolysis products of an alkene? What is the structural formula of the alkene?
Write a chemical equation for combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbon:
Butane
Write a chemical equation for combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbon:
Pentene
Write a chemical equation for combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbon:
Hexyne
Write a chemical equation for combustion reaction of the following hydrocarbon:
Toluene
Draw the cis and trans structures of hex-2-ene. Which isomer will have higher b.p. and why?
Why is benzene extra ordinarily stable though it contains three double bonds?
What are the necessary conditions for any system to be aromatic?
Explain why the following system is not aromatic?

Explain why the following system is not aromatic?
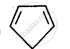
Explain why the following system is not aromatic?
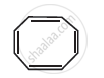
How will you convert benzene into p-nitrobromobenzene?
How will you convert benzene into m-nitrochlorobenzene?
How will you convert benzene into p -nitrotoluene?
How will you convert benzene into acetophenone?
In the alkane H3C–CH2–C(CH3)2–CH2–CH(CH3)2, identify 1°,2°,3° carbon atoms and give the number of H atoms bonded to each one of these.
What effect does branching of an alkane chain has on its boiling point?
Addition of HBr to propene yields 2-bromopropane, while in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields 1-bromopropane. Explain and give mechanism.
Write down the products of ozonolysis of 1, 2-dimethylbenzene (o-xylene). How does the result support Kekulé structure for benzene?
Arrange benzene, n-hexane and ethyne in decreasing order of acidic behaviour. Also give reason for this behaviour.
Why does benzene undergo electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty?
How would you convert the following compound into benzene?
Ethyne
How would you convert the following compound into benzene?
Ethene
How would you convert the following compound into benzene?
Hexane
Write structures of all the alkenes which on hydrogenation give 2-methylbutane.
Arrange the set of compound in order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+ Chlorobenzene, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene, p-nitrochlorobenzene.
Arrange the set of compound in order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+ Toluene, p-H3C–C6H4–NO2, p-O2N–C6H4–NO2.
Out of benzene, m–dinitrobenzene and toluene which will undergo nitration most easily and why?
Suggest the name of a Lewis acid other than anhydrous aluminium chloride which can be used during ethylation of benzene.
Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrate your answer by taking one example
Solutions for 13: Hydrocarbons
NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 13 - Hydrocarbons
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Mathematics Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC 13 (Hydrocarbons) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 13 Hydrocarbons are Classification of Hydrocarbons, Alkanes - Introduction, Nomenclature and Isomerism, Preparation of Alkanes from Unsaturated Hydrocarbons, Alkyl Halides and Carboxylic Acids, Physical Properties of Alkanes, Chemical Properties of Alkanes, Conformations (Ethane), Alkenes - Introduction, Structure of Double Bond (Ethene), Nomenclature, Isomerism, Preparation of Alkenes from Alkynes, Alkyl Halides, Vicinal Dihalides and Alcohols by Acidic Dehydration, Physical Properties of Alkenes, Chemical Properties of Alkenes, Alkynes - Introduction, Nomenclature and Isomerism, Structure of Triple Bond, Preparation of Alkynes from Calcium Carbide and Vicinal Dihalides, Physical Properties of Alkynes, Chemical Properties of Alkynes, Nomenclature and Isomerism, Structure of Benzene, Aromaticity (Huckel Rule), Preparation of Benzene, Physical Properties of Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Chemical Properties of Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Electrophilic Substitution Reactions, Mechanism of Electrophilic Substitution Reactions, Directive Influence of a Functional Group in Monosubstituted Benzene, Carcinogenicity and Toxicity, Aromatic Hydrocarbons.
Using NCERT Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 solutions Hydrocarbons exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 13, Hydrocarbons Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 13 - Hydrocarbons NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 13 - Hydrocarbons - Shaalaa.com](/images/9788174504944-chemistry-part-1-and-2-english-class-11_6:35966ca919014e8d958c20a41989d406.jpg)
