Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrate your answer by taking one example
Solution
Wurtz reaction is limited for the synthesis of symmetrical alkanes (alkanes with an even number of carbon atoms) In the reaction, two similar alkyl halides are taken as reactants and an alkane, containing double the number of carbon atoms, are formed. Example:
\[\ce{\underset{Bromomrthane}{CH3 - Br +}2Na + Br - CH3 ->[Dry ether] \underset{Ethane}{CH3 - CH3} + NaBr}\]
Wurtz reaction cannot be used for the preparation of unsymmetrical alkanes because if two dissimilar alkyl halides are taken as the reactants, then a mixture of alkanes is obtained as the products. Since the reaction involves free radical species, a side reaction also occurs to produce an alkene. For example, the reaction of bromomethane and iodoethane gives a mixture of alkanes.
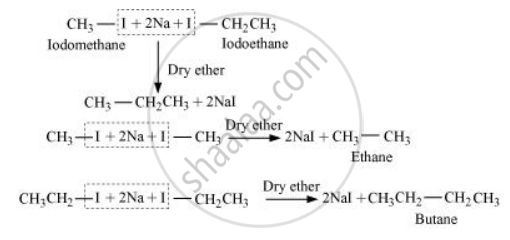
The boiling points of alkanes (obtained in the mixture) are very close. Hence, it becomes difficult to separate them
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Arrange the following alkyl halides in decreasing order of the rate of β– elimination reaction with alcoholic KOH.
| (A) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{H}\phantom{...}\\ |\phantom{...}\\ \ce{CH3 - C - CH2Br}\\ |\phantom{...}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{} \end{array}\] |
| (B) | \[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - Br}\] |
| (C) | \[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - Br}\] |
An alkyl halide C5H11Br (A) reacts with ethanolic KOH to give an alkene ‘B’, which reacts with Br2 to give a compound ‘C’, which on dehydrobromination gives an alkyne ‘D’. On treatment with sodium metal in liquid ammonia one mole of ‘D’ gives one mole of the sodium salt of ‘D’ and half a mole of hydrogen gas. Complete hydrogenation of ‘D’ yields a straight-chain alkane. Identify A, B, C and D. Give the reactions invovled.
Which alcohol can be converted most easily to alkenes?
Arrange the following alkyl halides in decreasing order of the rate of ~ elimination reaction with alcoholic KOH:
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - C - CH2Br}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{}
\end{array}\] - CH3 – CH2 – Br
- CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – Br
The major product formed in the dehydrohalogenation reaction of 2-Bromo pentane is Pent-2-ene. This product formation is based on the?
The major product in the following reaction is:
\[\ce{(A) ->[Cl2/hv] (B) ->[aq. KOH] (C) ->[O] CH3CHO}\]
Identify A, B and C:
What are A and B in the following reaction?
Major product of the reaction is: