Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Out of benzene, m–dinitrobenzene and toluene which will undergo nitration most easily and why?
Solution 1
The ease of nitration depends on the presence of electron density on the compound to form nitrates. Nitration reactions are examples of electrophilic substitution reactions where an electron-rich species is attacked by a nitronium ion (NO2–).
Now, CH3– group is electron donating and NO2– is electron withdrawing. Therefore, toluene will have the maximum electron density among the three compounds followed by benzene. On the other hand, m– Dinitrobenzene will have the least electron density. Hence, it will undergo nitration with difficulty. Hence, the increasing order of nitration is as follows:
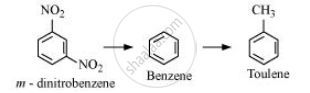
Solution 2
CH3 group is electron-donating while—NO2 group is electron-withdrawing. Therefore, maximum electron density will be in toluene, followed by benzene and least in m-dinitrobenzene. Therefore, the ease of nitration decreases in the order: toluene > benzene > m-dinitrobenzene
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Arrange the set of compound in order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+ Chlorobenzene, 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene, p-nitrochlorobenzene.
Arrange the set of compound in order of their decreasing relative reactivity with an electrophile, E+ Toluene, p-H3C–C6H4–NO2, p-O2N–C6H4–NO2.
Suggest the name of a Lewis acid other than anhydrous aluminium chloride which can be used during ethylation of benzene.
In an electrophilic substitution reaction of nitrobenzene, the presence of nitro group:
(i) Deactivates the ring by inductive effect.
(ii) Activates the ring by inductive effect.
(iii) Decreases the charge density at ortho and para position of the ring relative to meta position by resonance.
(iv) Increases the charge density at meta position relative to the ortho and para positions of the ring by resonance.
Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain.
Why does presence of a nitro group make the benzene ring less reactive in comparison to the unsubstituted benzene ring. Explain.
Choose an INCORRECT statement about the electrophilic substitution reaction mechanism from the following:
In Friedel-Crafts alkylation of aniline, one gets ______.
Excess of isobutane on reactions with Br2 in presence of light at 125°C gives which one of the following, as the major product?
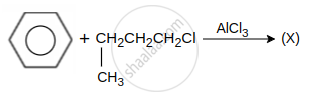
hydrocarbon (X) major product X is:
Benzene on nitration gives nitrobenzene in presence of HNO3 and H2SO4 mixture, where ______.
Which of the following would not give 2-phenylbutane as the major product in a Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction?
