Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Structure of Atom
3: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
▶ 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
5: States of Matter
6: Thermodynamics
7: Equilibrium
8: Redox Reactions
9: Hydrogen
10: The s-Block Elements
11: The p-Block Elements
12: Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
13: Hydrocarbons
14: Environmental Chemistry
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC NCERT for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11.
NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure EXERCISES [Pages 133 - 135]
Explain the Formation of a Chemical Bond.
Write Lewis dot symbols for atoms of the following elements: Mg, Na, B, O, N, Br.
Write Lewis symbols for the following atoms and ions: S and S2–.
Write Lewis symbols for the following atoms and ions: Al and Al3+.
Write Lewis symbols for the following atoms and ions H and H–.
Draw the Lewis structures for the following molecule and ion:
H2S
Draw the Lewis structures for the given molecule and ion:
SiCl4
Draw the Lewis structures for the given molecule and ion:
BeF2
Draw the Lewis structures for the given molecule and ion:
`"CO"_3^(2-)`
Draw the Lewis structures for the following molecule and ion:
HCOOH
Define octet rule.
Write the significance and limitations of octet rule.
Write the favourable factors for the formation of the ionic bond.
Discuss the shape of the following molecules using the VSEPR model:
BeCl2, BCl3, SiCl4, AsF5, H2S, PH3
Although geometries of NH3 and H2O molecules are distorted tetrahedral, bond angle in water is less than that of ammonia. Discuss.
How do you express the bond strength in terms of bond order?
Define the bond length.
Explain the important aspects of resonance with reference to the `"CO"_3^(2-)` ion.
H3PO3 can be represented by structures 1 and 2 shown below. Can these two structures be taken as the canonical forms of the resonance hybrid representing H3PO3? If not, give reasons for the same.
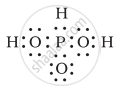 |
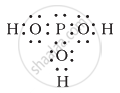 |
| (1) | (2) |
Write the resonance structure for SO3.
Write the resonance structures for NO2.
Write the resonance structures for `"NO"_3^(-)`.
Use Lewis symbols to show electron transfer between the following atoms to form cations and anions:-
K and S
Use Lewis symbols to show electron transfer between the following atoms to form cations and anions:
Ca and O
Use Lewis symbols to show electron transfer between the following atoms to form cations and anions:
Al and N
Although both CO2 and H2O are triatomic molecules, the shape of H2O molecule is bent while that of CO2 is linear. Explain this on the basis of dipole moment.
Write the significance/applications of dipole moment.
Define electronegativity.
How does electronegativity differ from electron gain enthalpy?
Explain with the help of suitable example polar covalent bond.
Arrange the bonds in order of increasing ionic character in the molecules: LiF, K2O, N2, SO2 and ClF3.
The skeletal structure of CH3COOH as shown below is correct, but some of the bonds are shown incorrectly. Write the correct Lewis structure for acetic acid.

Apart from tetrahedral geometry, another possible geometry for CH4 is square planar with the four H atoms at the corners of the square and the C atom at its centre. Explain why CH4 is not square planar?
Explain why BeH2 molecule has a zero dipole moment although the Be–H bonds are polar.
Which out of NH3 and NF3 has higher dipole moment and why?
What is meant by hybridisation of atomic orbitals?
Describe the shapes of sp, sp2,sp3 hybrid orbitals.
Describe the change in hybridisation (if any) of the Al atom in the following reaction.
\[\ce{AlCl_3 + Cl- -> AlCl_4-}\]
Is there any change in the hybridisation of B and N atoms as a result of the following reaction?
\[\ce{BF3 + NH3 → F3B.NH3}\]
Draw a diagram showing the formation of a double bond and a triple bond between carbon atoms in C2H4 and C2H2 molecules.
What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules?
C2H2
What is the total number of sigma and pi bonds in the following molecules?
C2H4
Considering x-axis as the internuclear axis which out of the following will not form a sigma bond and why? (a) 1s and 1s (b) 1s and 2px (c) 2py and 2py (d) 1s and 2s.
Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon atoms in the following molecules?
CH3–CH3
Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon atoms in the following molecules?
CH3–CH=CH2
Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon atoms in the following molecules?
CH3-CH2-OH
Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon atoms in the following molecules?
CH3-CHO
Which hybrid orbitals are used by carbon atoms in the following molecules?
CH3COOH
What do you understand by bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons? Illustrate by giving one example of each type.
Distinguish between a sigma and a pi bond.
Explain the formation of H2 molecule on the basis of valence bond theory.
Write the important conditions required for the linear combination of atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals.
Use molecular orbital theory to explain why the Be2 molecule does not exist.
Compare the relative stability of the following species and indicate their magnetic properties;
`"O"_2, "O"_2^+, "O"_2^-`(superoxide), `"O"_2^(2-)`(peroxide)
Write the significance of a plus and a minus sign shown in representing the orbitals.
Describe the hybridisation in case of PCl5. Why are the axial bonds longer as compared to equatorial bonds?
Define hydrogen bond. Is it weaker or stronger than the van der Waals forces?
What is meant by the term bond order?
Calculate the bond order of N2, O2, `"O"_2^+`and `"O"_2^-`?
Solutions for 4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 4 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Mathematics Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC 4 (Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure are Kossel and Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding, Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Octet Rule, Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Covalent Bond, Lewis Structures (Lewis Representation of Simple Molecules), Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Formal Charge, Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Limitations of the Octet Rule, Ionic or Electrovalent Bond, Bond Length, Bond Angle, Bond Enthalpy, Bond Order, Resonance Structures, Polarity of Bonds, Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR), Valence Bond Theory, Valence Bond Theory - Orbital Overlap Concept, Valence Bond Theory - Directional Properties of Bonds, Valence Bond Theory - Overlapping of Atomic Orbitals, Valence Bond Theory - Types of Overlapping and Nature of Covalent Bonds, Valence Bond Theory - Strength of Sigma (σ) bond and pi (π) bond, Hybridisation - Introduction, Types of Hybridisation, Hybridisation of Elements Involving d Orbitals, Molecular Orbital Theory - Introduction, Formation of Molecular Orbitals - Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO), Conditions for the Combination of Atomic Orbitals, Types of Molecular Orbitals, Energy Level Diagram for Molecular Orbitals, Electronic Configuration and Molecular Behaviour, Bonding in Some Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules, Hydrogen Bonding - Introduction, Cause of Formation of Hydrogen Bond, Types of Hydrogen Bonding, Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Numericals, States of Matter:- Gases and Liquids Numericals, Kossel and Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding, Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Octet Rule, Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Covalent Bond, Lewis Structures (Lewis Representation of Simple Molecules), Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Formal Charge, Kossel-lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding - Limitations of the Octet Rule, Ionic or Electrovalent Bond, Bond Length, Bond Angle, Bond Enthalpy, Bond Order, Resonance Structures, Polarity of Bonds, Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR), Valence Bond Theory, Valence Bond Theory - Orbital Overlap Concept, Valence Bond Theory - Directional Properties of Bonds, Valence Bond Theory - Overlapping of Atomic Orbitals, Valence Bond Theory - Types of Overlapping and Nature of Covalent Bonds, Valence Bond Theory - Strength of Sigma (σ) bond and pi (π) bond, Hybridisation - Introduction, Types of Hybridisation, Hybridisation of Elements Involving d Orbitals, Molecular Orbital Theory - Introduction, Formation of Molecular Orbitals - Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO), Conditions for the Combination of Atomic Orbitals, Types of Molecular Orbitals, Energy Level Diagram for Molecular Orbitals, Electronic Configuration and Molecular Behaviour, Bonding in Some Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules, Hydrogen Bonding - Introduction, Cause of Formation of Hydrogen Bond, Types of Hydrogen Bonding, Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Numericals, States of Matter:- Gases and Liquids Numericals.
Using NCERT Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 solutions Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 4 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 4 - Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Shaalaa.com](/images/9788174504944-chemistry-part-1-and-2-english-class-11_6:35966ca919014e8d958c20a41989d406.jpg)
