Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define the bond length.
Solution 1
Bond length is defined as the equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule.
Bond lengths are expressed in terms of Angstrom (10–10 m) or picometer
(10–12 m) and are measured by spectroscopic X-ray diffractions and electron-diffraction techniques.
In an ionic compound, the bond length is the sum of the ionic radii of the constituting atoms (d = r+ + r–). In a covalent compound, it is the sum of their covalent radii (d = rA+ rB).
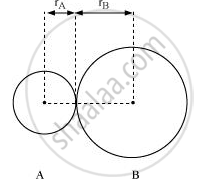
Solution 2
Bond-length: It is the equilibrium distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms in a molecule. Bond-lengths are measured by spectroscopic methods
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In which of the following molecule/ion all the bonds are not equal?
Which of the following statements are correct about \[\ce{CO^{2-}3}\]?
(i) The hybridisation of central atom is sp3.
(ii) Its resonance structure has one \[\ce{C - O}\] single bond and two \[\ce{C = O}\] double bonds.
(iii) The average formal charge on each oxygen atom is 0.67 units.
(iv) All \[\ce{C - O}\] bond lengths are equal.
All the \[\ce{C - O}\] bonds in carbonate ion \[\ce{(CO^{2-}3)}\] are equal in length. Explain.
Describe hybridisation in the case of \[\ce{PCl5}\] and \[\ce{SF6}\]. The axial bonds are longer as compared to equatorial bonds in \[\ce{PCl5}\] whereas in \[\ce{SF6}\] both axial bonds and equatorial bonds have the same bond length. Explain.
In a covalent bond, ______ the bond length ______ is the energy required to break the bond.
