Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Structure of Atom
3: Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
4: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
5: States of Matter
6: Thermodynamics
7: Equilibrium
8: Redox Reactions
9: Hydrogen
10: The s-Block Elements
11: The p-Block Elements
▶ 12: Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
13: Hydrocarbons
14: Environmental Chemistry
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 12: Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 12 of CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC NCERT for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11.
NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques EXERCISES [Pages 370 - 372]
What is hybridization state of each carbon atom in the following compound?
CH2 = C = O
What is hybridization state of each carbon atom in the following compound?
CH3CH = CH2
What is hybridization state of each carbon atom in the following compound?
(CH3)2CO
What is hybridization state of each carbon atom in the following compound?
CH2 = CHCN
What is hybridization state of each carbon atom in the following compound?
C6H6
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the following molecules:
C6H6
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the following molecules:
C6H12
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the following molecules:
CH2Cl2
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the following molecules:
CH2 = C = CH2
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the following molecules:
CH3NO2
Indicate the σ and π bonds in the following molecule:
HCONHCH3
Write bond line formulas for Isopropyl alcohol.
Write bond line formulas for 2,3-Dimethyl butanal.
Write bond line formulas for Heptan-4-one.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound.
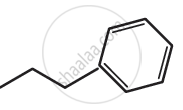
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound:
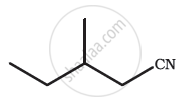
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound:
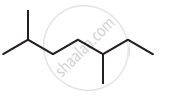
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound:
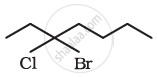
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound:
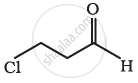
Give the IUPAC names of the following compound:
Cl2CHCH2OH
Which of the following represent the correct IUPAC name for the compound concerned?
2, 2-Dimethylpentane
2-Dimethylpentane
Which of the following represent the correct IUPAC name for the compound concerned?
2, 4, 7-Trimethyloctane
2, 5, 7-Trimethyloctane
Which of the following represent the correct IUPAC name for the compound concerned?
2-Chloro-4-methylpentane
4-Chloro-2-methylpentane
Which of the following represent the correct IUPAC name for the compound concerned?
But-3-yn-1-ol
But-4-ol-1-yne
Draw a formula for the first five members of the homologous series beginning with the given compound.
H–COOH
Draw a formula for the first five members of the homologous series beginning with the given compound.
CH3COCH3
Draw a formula for the first five members of the homologous series beginning with the given compound.
H–CH=CH2
Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for:
2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for
2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid
Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s) present, if any, for
Hexanedial
Identify the functional group in the following compound.

Identify the functional group in the following compound.
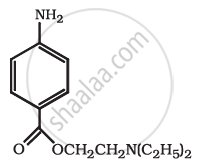
Identify the functional group in the following compound.
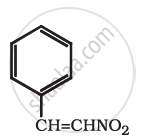
Which of the two: O2NCH2CH2O– or CH3CH2O–is expected to be more stable and why?
Explain why alkyl groups act as electron donors when attached to a π system
Draw the resonance structure for the following compound. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
C6H5OH
Draw the resonance structure for the following compound. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
C6H5NO2
Draw the resonance structure for the following compound. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
CH3CH = CHCHO
Draw the resonance structure for the following compound. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
C6H5 – CHO
Draw the resonance structure for the following compound. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
\[\ce{C6H5 - \overset{+}{C}H2}\]
Draw the resonance structure for the following compound. Show the electron shift using curved-arrow notation.
\[\ce{CH3CH = CH\overset{+}{C}H2}\]
What are electrophiles and nucleophiles? Explain with examples.
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equation as nucleophiles or electrophiles:
\[\ce{CH3COOH + \underline{\ce{H}\overset{-}{\ce{O}}} -> CH3COO^- + H2O }\]
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equation as nucleophiles or electrophiles:
\[\ce{CH3COCH3 + \underline{\overset{-}{\ce{C}}\ce{N}} -> (CH3)2C(CN)(OH)}\]
Identify the reagents shown in bold in the following equation as nucleophiles or electrophiles:
\[\ce{C6H6 + \underline{\text{CH}_3\overset{+}{\ce{C}}{\ce{O}}} -> C6H5COCH3}\]
Classify the following reaction in one of the reaction type studied in this unit.
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + HS– → CH3CH2SH + Br–}\]
Classify the following reaction in one of the reaction type studied in this unit.
\[\ce{(CH3)2 C = CH2 + HCl → (CH3)2 ClC–CH3}\]
Classify the following reaction in one of the reaction type studied in this unit.
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + HO– → CH2 = CH2 + H2O + Br–}\]
Classify the following reaction in one of the reaction type studied in this unit.
\[\ce{(CH3)3 C – CH2 OH + HBr → (CH3)2 CBrCH2CH3 + H2O}\]
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?

What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{D}\phantom{......}\ce{H}\\
\backslash\phantom{......}/\\
\ce{C = C}\\
\phantom{...}/\phantom{......}\backslash\phantom{...}\\\ce{H}\phantom{.......}\ce{D}
\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{D}\phantom{......}\ce{D}\\
\backslash\phantom{......}/\\
\ce{C = C}\\
\phantom{...}/\phantom{......}\backslash\phantom{...}\\\ce{H}\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\end{array}\]
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{^+OH}\\||\\
\ce{H - C - OH}\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{OH}\phantom{.}\\|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{H - C^+ - OH}\end{array}\]
For the following bond cleavages, use curved arrows to show the electron flow and classify homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
\[\ce{CH3O - OCH3 -> CH3\overset\bullet{\text{O}} + \overset\bullet{\text{O}}CH3}\]
For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
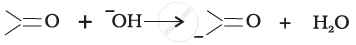
For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
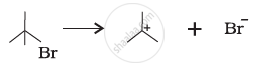
For the following bond cleavages, use curved-arrows to show the electron flow and classify as homolysis or heterolysis. Identify reactive intermediate produced as free radical, carbocation and carbanion.
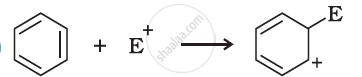
Which electron displacement effect explains the following correct orders of acidity of the carboxylic acids?
\[\ce{Cl3CCOOH > Cl2CHCOOH > ClCH2COOH}\]
Which electron displacement effect explains the following correct orders of acidity of the carboxylic acids?
\[\ce{CH3CH2COOH > (CH3)2CHCOOH > (CH3)3C.COOH}\]
Explain the terms Inductive and Electromeric effects.
Give a brief description of the principle of the following technique taking an example.
Crystallisation
Give a brief description of the principle of the following technique taking an example.
Distillation
Give a brief description of the principle of the following technique taking an example.
Chromatography
Describe the method, which can be used to separate two compounds with different solubilities in a solvent S.
What is the difference between distillation, distillation under reduced pressure and steam distillation ?
Discuss the chemistry of Lassaigne’s test.
Differentiate between the principle of estimation of nitrogen in an organic compound by Dumas method.
Differentiate between the principle of estimation of nitrogen in an organic compound by Kjeldahl’s method.
Discuss the principle of estimation of halogens present in an organic compound.
Discuss the principle of estimation of sulphur present in an organic compound.
Discuss the principle of estimation of phosphorus present in an organic compound.
Explain the principle of paper chromatography.
Why is nitric acid added to sodium extract before adding silver nitrate for testing halogens?
Explain the reason for the fusion of an organic compound with metallic sodium for testing nitrogen, sulphur and halogens.
Name a suitable technique of separation of the components from a mixture of calcium sulphate and camphor.
Explain, why an organic liquid vaporises at a temperature below its boiling point in its steam distillation?
Will CCl4 give white precipitate of AgCl on heating it with silver nitrate? Give reason for your answer.
Why is a solution of potassium hydroxide used to absorb carbon dioxide evolved during the estimation of carbon present in an organic compound?
Why is it necessary to use acetic acid and not sulphuric acid for acidification of sodium extract for testing sulphur by lead acetate test?
An organic compound contains 69% carbon and 4.8% hydrogen, the remainder being oxygen. Calculate the masses of carbon dioxide and water produced when 0.20 g of this substance is subjected to complete combustion.
A sample of 0.50 g of an organic compound was treated according to Kjeldahl’s method. The ammonia evolved was absorbed in 50 mL of 0.5 M H2SO4. The residual acid required 60 mL of 0.5 M solution of NaOH for neutralisation. Find the percentage composition of nitrogen in the compound.
0.3780 g of an organic chloro compound gave 0.5740 g of silver chloride in Carius estimation. Calculate the percentage of chlorine present in the compound.
In the estimation of sulphur by Carius method, 0.468 g of an organic sulphur compound afforded 0.668 g of barium sulphate. Find out the percentage of sulphur in the given compound.
In the organic compound CH2 = CH – CH2 – CH2 – C ≡ CH, the pair of hybridized orbitals involved in the formation of: C2 – C3 bond is ______.
sp – sp2
sp – sp3
sp2 – sp3
sp3– sp3
In Lassaigne’s test for nitrogen in an organic compound, the Prussian blue colour is obtained due to the formation of ______.
Na4[Fe(CN)6]
Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
Fe2[Fe(CN)6]
Fe3[Fe(CN)6]4
Which of the following carbocation is most stable?
\[\ce{(CH3)3C*^+CH2}\]
\[\ce{(CH3)3^+C}\]
\[\ce{CH3CH2^+CH2}\]
\[\ce{CH3^+CH CH2C}\]
The best and latest technique for isolation, purification and separation of organic compounds is ______.
Crystallisation
Distillation
Sublimation
Chromatography
The reaction: \[\ce{CH_3CH_2I + KOH_{(aq)} -> CH_3CH_2OH + KI}\] is classified as ______.
electrophilic substitution
nucleophilic substitution
elimination
addition
Solutions for 12: Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Mathematics Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC 12 (Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 12 Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques are Tetravalence of Carbon - Shapes of Organic Compounds, Complete, Condensed and Bond-line Structural Formulas, Three-dimensional Representation of Organic Molecules, Classification of Organic Compounds, The IUPAC System of Nomenclature, IUPAC Nomenclature of Alkanes, Nomenclature of Organic Compounds Having Functional Group(s), Nomenclature of Substituted Benzene Compounds, Fission of a Covalent Bond, Nucleophiles and Electrophiles, Electron Movement in Organic Reactions, Electron Displacement Effects in Covalent Bonds, Inductive Effect, Resonance Structure, Resonance Effect, Electromeric Effect (E Effect), Hyperconjugation, Types of Organic Reactions and Mechanisms, Introduction of Methods of Purification of Organic Compounds, Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds - Detection of Carbon and Hydrogen, Quantitative Analysis of Nitrogen, Quantitative Analysis of Halogens, Quantitative Analysis of Sulphur, Quantitative Analysis of Phosphorus, Quantitative Analysis of Oxygen, Simple Distillation Method, Chromatography Method, Isomerism, Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds - Detection of Other Elements, Quantitative Analysis of Carbon and Hydrogen, Crystallisation Method, Sublimation Method, Solvent Extraction (Using a Separating Funnel Method), Tetravalence of Carbon - Shapes of Organic Compounds, Complete, Condensed and Bond-line Structural Formulas, Three-dimensional Representation of Organic Molecules, Classification of Organic Compounds, The IUPAC System of Nomenclature, IUPAC Nomenclature of Alkanes, Nomenclature of Organic Compounds Having Functional Group(s), Nomenclature of Substituted Benzene Compounds, Fission of a Covalent Bond, Nucleophiles and Electrophiles, Electron Movement in Organic Reactions, Electron Displacement Effects in Covalent Bonds, Inductive Effect, Resonance Structure, Resonance Effect, Electromeric Effect (E Effect), Hyperconjugation, Types of Organic Reactions and Mechanisms, Introduction of Methods of Purification of Organic Compounds, Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds - Detection of Carbon and Hydrogen, Quantitative Analysis of Nitrogen, Quantitative Analysis of Halogens, Quantitative Analysis of Sulphur, Quantitative Analysis of Phosphorus, Quantitative Analysis of Oxygen, Simple Distillation Method, Chromatography Method, Isomerism, Qualitative Analysis of Organic Compounds - Detection of Other Elements, Quantitative Analysis of Carbon and Hydrogen, Crystallisation Method, Sublimation Method, Solvent Extraction (Using a Separating Funnel Method).
Using NCERT Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 solutions Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 12, Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques NCERT solutions for Chemistry - Part 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 chapter 12 - Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques - Shaalaa.com](/images/9788174504944-chemistry-part-1-and-2-english-class-11_6:35966ca919014e8d958c20a41989d406.jpg)
