Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How would you account for the irregular variation of ionization enthalpies (first and second) in the first series of the transition elements?
Solution 1
Ionization enthalpies are found to increase in the given series due to a continuous filling of the inner d-orbitals. The irregular variations of ionization enthalpies can be attributed to the extra stability of configurations such as d0, d5 and d10. Since these states are exceptionally stable, their ionization enthalpies are very high.
In terms of first ionization energy, Cr has low ionization energy. This is because after losing one electron, it attains the stable configuration (3d5). On the other hand, Zn has exceptionally high first ionization energy, as an electron has to be removed from stable and fully-filled orbitals (3d10 4s2).
The second ionization energies are higher than the first since it becomes difficult to remove an electron when an electron has already been removed. Also, elements like Cr and Cu have exceptionally high second ionization energies, as after losing the first electron, they have attained the stable configuration (Cr+: 3d5 and Cu+: 3d10). Hence, taking out one electron more from this stable configuration will require a lot of energy.
Solution 2
The irregular variations in ionization enthalpy are due to differences in the stability of different 3d configurations (e.g., d0, d5, d10 are unusually stable).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the series Sc (Z = 21) to Zn (Z = 30), the enthalpy of atomization of zinc is the lowest, i.e., 126 kJ mol−1. Why?
What are alloys?
Use Hund’s rule to derive the electronic configuration of Ce3+ ion and calculate its magnetic moment on the basis of ‘spin-only’ formula.
Compare the general characteristics of the first series of the transition metals with those of the second and third series metals in the respective vertical columns. Give special emphasis on the following point:
Electronic configurations
Give reasons Iron has the higher enthalpy of atomization than that of copper.
Why does the density of transition elements increase from Titanium to Copper? (at. no. Ti = 22,
Cu = 29)
Which of the following statements is not correct?
Why does copper not replace hydrogen from acids?
A solution of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] on reduction yields either a colourless solution or a brown precipitate or a green solution depending on pH of the solution. What different stages of the reduction do these represent and how are they carried out?
The second and third rows of transition elements resemble each other much more than they resemble the first row. Explain why?
Match the catalysts given in Column I with the processes given in Column II.
| Column I (Catalyst) | Column II (Process) |
| (i) \[\ce{Ni}\] in the presence of hydrogen | (a) Zieglar Natta catalyst |
| (ii) \[\ce{Cu2C12}\] | (b) Contact process |
| (iii) \[\ce{V2O5}\] | (c) Vegetable oil to ghee |
| (iv) Finely divided iron | (d) Sandmeyer reaction |
| (v) \[\ce{TiCl4 + Al (CH3)3}\] | (e) Haber's Process |
| (f) Decomposition of KCIO3 |
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
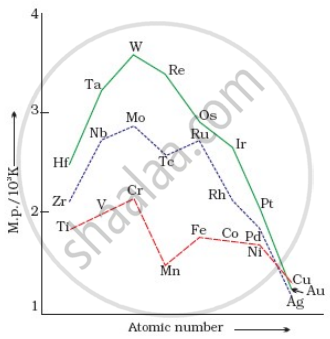
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
Which of the following is non-metallic?
Sodium this sulphate is used in photography because of its:-
The value of Δ0 for \[\ce{RhCl^{3-}6}\] is 243 KJ/mol which wavelength of light will promote an electron from. The colour of the complex is ______.
The disproportionation of \[\ce{MnO^{2-}_4}\] in acidic medium resulted in the formation of two manganese compounds A and B. If the oxidation state of Mn in B is smaller than that of A, then the spin-only magnetic moment (µ) value of B in BM is ______. (Nearest integer)
Assertion (A): Transition metals have high enthalpy of atomisation.
Reason (R): Greater number of unpaired electrons in transition metals results in weak metallic bonding.
Write the number of unpaired electrons in Cr3+.
(Atomic number of Cr = 24)
In order to protect iron from corrosion, which one will you prefer as a sacrificial electrode, Ni or Zn? Why? (Given standard electrode potentials of Ni, Fe and Zn are -0.25 V, -0.44 V and -0.76 V respectively.)
Explain the magnetic properties of d-block (or transition) elements.
