Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
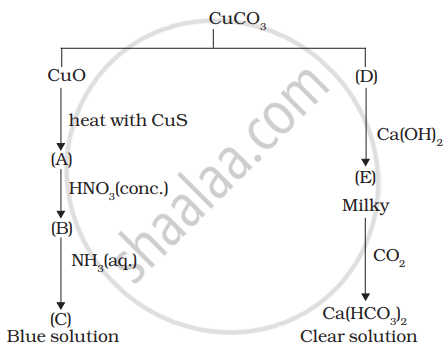
Identify A to E and also explain the reactions involved.
Solution
A = \[\ce{Cu}\]
B = \[\ce{Cu(NO3)2}\]
C = \[\ce{[Cu(NH3)4]}\]
D = \[\ce{CO2}\]
E = \[\ce{CaCO3}\]
F = \[\ce{Cu2[Fe(CN)6]}\]
G = \[\ce{Ca (HCO3)2}\]
\[\ce{CuCO3 -> CuO + CO2}\]
\[\ce{CuO + CuS -> \underset{(A)}{Cu} + SO2}\]
\[\ce{Cu + 4HNO3 (Conc) -> Cu \underset{(B)}{(NO3)2} + 2NO + 2H2O}\]
\[\ce{\underset{(B)}{Cu^2+} + NH3 -> \underset{(C)}{[Cu(NH3)4]}}\]
\[\ce{Ca(OH)2 + \underset{(D)}{CO2} -> \underset{(E)}{CaCO3} + H2O}\]
\[\ce{CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O -> Ca(HCO3)2}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How would you account for the following?
Transition metals exhibit variable oxidation states.
The elements of 3d transition series are given as: Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co
Answer the following: Which element has the highest m.p?
What can be inferred from the magnetic moment value of the following complex species?
| Example | Magnetic Moment (BM) |
| K2[MnCl4] | 5.9 |
Write the formula of an oxo-anion of Chromium (Cr) in which it shows the oxidation state equal to its group number
Following are the transition metal ions of 3d series:
Ti4+, V2+, Mn3+, Cr3+
(Atomic numbers: Ti = 22, V = 23, Mn = 25, Cr = 24)
Answer the following:
1) Which ion is most stable in an aqueous solution and why?
2) Which ion is a strong oxidising agent and why?
3) Which ion is colourless and why?
On strong heating AgNO3, the gases evolved are:-
Passing H2S gas into a mixture of Mn2+ and Ni2+, Cu2+, ions in an acidified aqueous solution precipitates.
Which of the following transition metal is not coloured?
How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals different from that of p-block elements?
What is the oxidation state of chromium in chromate ion and dichromate ion?
