Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Identify the following diagram, label it and prepare a chart of characteristics.

Solution
T.S. of dicot root-

- Epiblema:
It is the outermost single layer of cells without cuticles. Some epidermal cells prolong to form unicellular root hairs. - Cortex:
It is made up of many layers of thin walled parenchyma cells. Cortical cells store food and water. - Exodermis:
After the death of epiblema, the outer layer of the cortex becomes cutinized and is called Exodermis. - Endodermis:
The innermost layer of cortex is called Endodermis. The cells are barrel-shaped and their radial walls bear Casparian strip or Casparian bands composed of suberin. Near the protoxylem, there are unthickened passage cells. - Stele:
It consists of pericycle, vascular bundles and pith.
a. Pericycle:
Next to the endodermis, there is a single layer of thin walled parenchyma cells called pericycle. It forms outermost layer of stele or vascular cylinder.
b. Vascular bundle:
Vascular bundles are radial. Xylem and Phloem occur in separate patches arranged on alternate radii. Xylem is exarch in root that means protoxylem vessels are towards periphery and metaxylem elements are towards centre. Xylem bundles vary from two to six number, i.e. they may be diarch, triarch, tetrarch, etc. Connective tissue: A parenchymatous tissue is present in between xylem and phloem.
c. Pith:
The central part of stele is called pith. It is narrow and made up of parenchymatous cells, with or without intercellular spaces. - At a later stage cambium ring develops between the xylem and phloem causing secondary growth.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
A fresh section was taken by a student but he was very disappointed because there were only a few green and most colourless cells. Teacher provided a pink colour solution. The section was immersed in this solution and when observed it was much clearer. What is magic?
Answer the following question.
A student was observing a slide with no label under a microscope. The section had some vascular bundles scattered in the ground tissue. It is a section of a monocot stem! He exclaimed. No! it is a section of fern rachis, said the teacher. Teacher told to observe vascular bundle again. Student agreed, Why?
Answer the following question.
Student while observing a slide of leaf section observed many stomata on the upper surface. He thought he has placed slide upside down. Teacher confirmed it is rightly placed. Explain.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
T. S. of Dicot leaf
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
T. S. of dicot stem
Write the information related to the diagram given below.

Identify the following diagram, label it and prepare a chart of characteristics.
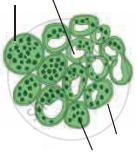
Identify the following diagram, label it and prepare a chart of characteristics.

Identify the following diagram, label it and prepare a chart of characteristics.

Distinguish between dicot and monocot leaf on the basis of following characters.
| Characters | Dicot leaf | Monocot leaf |
| Stomata | ||
| Intercellular space | ||
| Venation | ||
| Vascular bundle | ||
| Mesophyll cells |
