Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Identify the following diagram, label it and prepare a chart of characteristics.

Solution
V. S. of dicot leaf-

- Structure of dorsiventral leaf:
The mesophyll tissue is differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma in a dorsiventral leaf. This type is very common in dicot leaf. The different parts of this leaf are as follows: - Upper epidermis:
It consists of a single layer of tightly packed rectangular, barrel shaped, parenchymatous cells which are devoid of chloroplast. A distinct layer of cuticle lies on the outside of the epidermis. Stomata are generally absent. - Mesophyll:
Between upper and lower epidermis, there is chloroplast-containing photosynthetic tissue called mesophyll It is differentiated into Palisade parenchyma and Spongy parenchyma.
- Palisade parenchyma:
Palisade parenchyma is present below upper epidermis and consists of closely packed elongated cells. The cells contain abundant chloroplasts and help in photosynthesis. - Spongy parenchyma:
Spongy parenchyma is present below palisade tissue and consists of loosely arranged irregularly shaped cells with intercellular spaces. The spongy parenchyma cells contain chloroplast and are in contact with the atmosphere through stomata.
- Vascular system:
It is made up of a number of vascular bundles of varying size depending upon the venation. Each one is surrounded by a thin layer of parenchymatous cells called bundle sheath. Vascular bundles are closed. Xylem lies towards upper epidermis and phloem towards lower epidermis. Cambium is absent, hence there is no secondary growth in the leaf. - Lower epidermis:
It consists of a single layer of compactly arranged rectangular, parenchymatous cells. A thin layer of cuticle is also present. The lower epidermis contains a large number of microscopic pores called stomata. There is an air-space called substomatal chamber at each stoma.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
While observing a section, many scattered vascular bundles could be seen. Teacher said, in spite of this large number the stem cannot grow in girth. Why?
Answer the following question.
A student was observing a slide with no label under a microscope. The section had some vascular bundles scattered in the ground tissue. It is a section of a monocot stem! He exclaimed. No! it is a section of fern rachis, said the teacher. Teacher told to observe vascular bundle again. Student agreed, Why?
Answer the following question.
Student while observing a slide of leaf section observed many stomata on the upper surface. He thought he has placed slide upside down. Teacher confirmed it is rightly placed. Explain.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
T. S. of Dicot leaf
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
T. S. of dicot stem
Write the information related to the diagram given below.

Identify the following diagram, label it and prepare a chart of characteristics.

Identify the following diagram, label it and prepare a chart of characteristics.
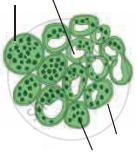
Identify the following diagram, label it and prepare a chart of characteristics.

Distinguish between dicot and monocot leaf on the basis of following characters.
| Characters | Dicot leaf | Monocot leaf |
| Stomata | ||
| Intercellular space | ||
| Venation | ||
| Vascular bundle | ||
| Mesophyll cells |
