Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If the centroid of a triangle is at (4, −2) and two of its vertices are (3, −2) and (5, 2) then find the third vertex of the triangle
Solution
Let the vertices of a triangle be A(3, −2), B(5, 2) and C(x3, y3)
Centroid of a triangle is (4, −2)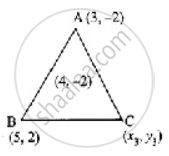
Centroid of a triangle G = `((x_1 + x_2 + x_3)/3, (y_1 + y_2 + y_3)/3)`
(4, −2) = `((3 + 5 + x_3)/3, (-2 + 2 + y_3)/3)`
= `((8 + x_3)/3, (y_3)/3)`
∴ `(8 + x_3)/3` = 4
8 + x3 = 12
x3 = 12 – 8
= 4
and
`(y_3)/3` = −2
y3 = −6
∴ The third vertex is (4, −6)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the centroid of the triangle whose vertices are (2, −4), (−3, −7) and (7, 2)
Find the centroid of the triangle whose vertices are (−5, −5), (1, −4) and (−4, −2)
Find the length of median through A of a triangle whose vertices are A(−1, 3), B(1, −1) and C(5, 1)
The vertices of a triangle are (1, 2), (h, −3) and (−4, k). If the centroid of the triangle is at the point (5, −1) then find the value of `sqrt(("h" + "k")^2 + ("h" + 3"k")^2`
Orthocentre and centroid of a triangle are A(−3, 5) and B(3, 3) respectively. If C is the circumcentre and AC is the diameter of this circle, then find the radius of the circle
ABC is a triangle whose vertices are A(3, 4), B(−2, −1) and C(5, 3). If G is the centroid and BDCG is a parallelogram then find the coordinates of the vertex D.
If `(3/2, 5), (7, (-9)/2)` and `(13/2, (-13)/2)` are mid-points of the sides of a triangle, then find the centroid of the triangle
