Advertisements
Chapters
2: Real Numbers
3: Algebra
4: Geometry
▶ 5: Coordinate Geometry
6: Trigonometry
7: Mensuration
8: Statistics
9: Probability
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board chapter 5 - Coordinate Geometry Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board chapter 5 - Coordinate Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Coordinate Geometry
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board 5 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 5.1 [Pages 192 - 193]
Plot the following point in the coordinate system and identify the quadrant.
P(−7, 6)
Plot the following point in the coordinate system and identify the quadrant.
Q(7, −2)
Plot the following point in the coordinate system and identify the quadrant.
R(−6, −7)
Plot the following point in the coordinate system and identify the quadrant.
S(3, 5)
Plot the following point in the coordinate system and identify the quadrant.
T(3, 9)
Write down the abscissa and ordinate of the following.
P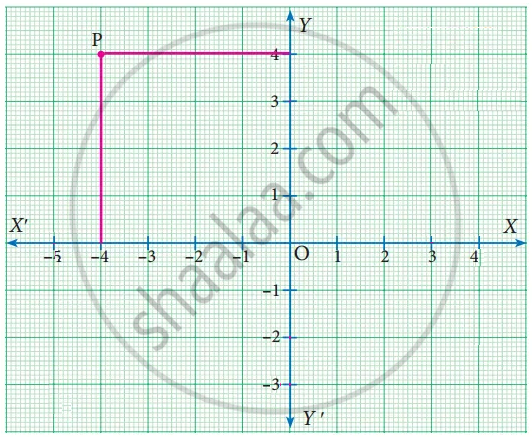
Write down the abscissa and ordinate of the following.
Q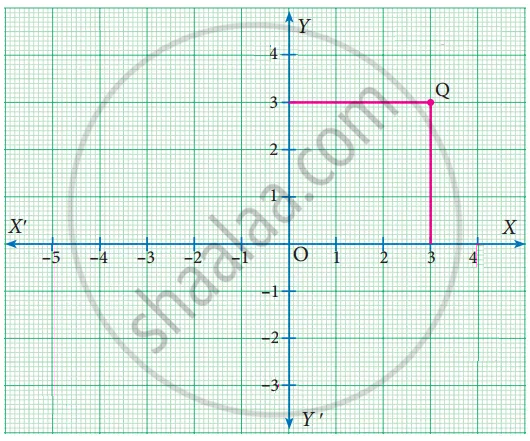
Write down the abscissa and ordinate of the following.
R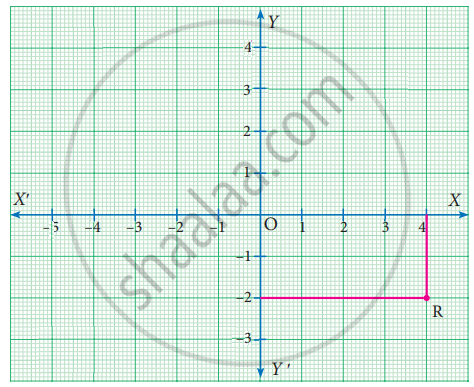
Write down the abscissa and ordinate of the following.
S
Plot the following points in the coordinate plane and join them. What is your conclusion about the resulting figure?
(−5, 3) (−1, 3) (0, 3) (5, 3)
Plot the following points in the coordinate plane and join them. What is your conclusion about the resulting figure?
(0, −4) (0, −2) (0, 4) (0, 5)
Plot the following points in the coordinate plane. Join them in order. What type of geometrical shape is formed?
(0, 0) (−4, 0) (−4, −4) (0, −4)
Plot the following points in the coordinate plane. Join them in order. What type of geometrical shape is formed?
(−3, 3) (2, 3) (−6, −1) (5, −1)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board 5 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 5.2 [Pages 202 - 203]
Find the distance between the following pair of points
(1, 2) and (4, 3)
Find the distance between the following pair of points
(3, 4) and (−7, 2)
Find the distance between the following pair of points
(a, b) and (c, b)
Find the distance between the following pair of points
(3, −9) and (−2, 3)
Determine whether the given set of points are collinear or not
(7, −2), (5, 1), (3, 4)
Determine whether the given set of points are collinear or not
(a, −2), (a, 3), (a, 0)
Show that the following points taken in order to form an isosceles triangle
A(5, 4), B(2, 0), C(−2, 3)
Show that the following points taken in order to form an isosceles triangle
A(6, −4), B(−2, −4), C(2, 10)
Show that the following points taken in order to form an equilateral triangle
`"A"(2, 2), "B"(-2, -2), "C"(-2sqrt(3), 2sqrt(3))`
Show that the following points taken in order to form an equilateral triangle
`"A"(sqrt(3), 2), "B"(0, 1), "C"(0, 3)`
Show that the following points taken in order to form the vertices of a parallelogram
A(−3, 1), B(−6, −7), C(3, −9) and D(6, −1)
Show that the following points taken in order to form the vertices of a parallelogram
A(−7, −3), B(5, 10), C(15, 8) and D(3, −5)
Verify that the following points taken in order to form the vertices of a rhombus
A(3, −2), B(7, 6), C(−1, 2) and D(−5, −6)
Verify that the following points taken in order to form the vertices of a rhombus
A(1, 1), B(2, 1), C(2, 2) and D(1, 2)
A(−1, 1), B(1, 3) and C(3, a) are point and if AB = BC, then find ‘a’
The abscissa of a point A is equal to its ordinate, and its distance from the point B(1, 3) is 10 units, What are the coordinates of A?
The point (x, y) is equidistant from the points (3, 4) and (−5, 6). Find a relation between x and y
Let A(2, 3) and B(2, −4) be two points. If P lies on the x-axis, such that AP = `3/7` AB, find the coordinates of P.
Show that the point (11, 2) is the centre of the circle passing through the points (1, 2), (3, −4) and (5, −6)
The radius of a circle with centre at origin is 30 units. Write the coordinates of the points where the circle intersects the axes. Find the distance between any two such points.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board 5 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 5.3 [Page 208]
Find the mid-point of the line segment joining the points
(−2, 3) and (−6, −5)
Find the mid-point of the line segment joining the points
(8, −2) and (−8, 0)
Find the mid-point of the line segment joining the points
(a, b) and (a + 2b, 2a – b)
Find the mid-point of the line segment joining the points
`(1/2, (-3)/7)` and `(3/2, (-11)/7)`
The centre of a circle is (−4, 2). If one end of the diameter of the circle is (−3, 7) then find the other end
If the mid-point (x, y) of the line joining (3, 4) and (p, 7) lies on 2x + 2y + 1 = 0, then what will be the value of p?
The mid-point of the sides of a triangle are (2, 4), (−2, 3) and (5, 2). Find the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle
O(0, 0) is the centre of a circle whose one chord is AB, where the points A and B are (8, 6) and (10, 0) respectively. OD is the perpendicular from the centre to the chord AB. Find the coordinates of the mid-point of OD.
The points A(−5, 4), B(−1, −2) and C(5, 2) are the vertices of an isosceles right-angled triangle where the right angle is at B. Find the coordinates of D so that ABCD is a square
The points A(−3, 6), B(0, 7) and C(1, 9) are the mid-points of the sides DE, EF and FD of a triangle DEF. Show that the quadrilateral ABCD is a parallelogram.
A(−3, 2), B(3, 2) and C(−3, −2) are the vertices of the right triangle, right angled at A. Show that the mid-point of the hypotenuse is equidistant from the vertices
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board 5 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 5.4 [Page 214]
Find the coordinates of the point which divides the line segment joining the points A(4, −3) and B(9, 7) in the ratio 3 : 2
In what ratio does the point P(2, −5) divide the line segment joining A(−3, 5) and B(4, −9)
Find the coordinates of a point P on the line segment joining A(1, 2) and B(6, 7) in such a way that AP = `2/5` AB
Find the coordinates of the points of trisection of the line segment joining the points A(−5, 6) and B(4, −3)
The line segment joining A(6, 3) and B(−1, −4) is doubled in length by adding half of AB to each end. Find the coordinates of the new end points.
Using section formula, show that the points A(7, −5), B(9, −3) and C(13, 1) are collinear
A line segment AB is increased along its length by 25% by producing it to C on the side of B. If A and B have the coordinates (−2, −3) and (2, 1) respectively, then find the coordinates of C.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board 5 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 5.5 [Pages 217 - 218]
Find the centroid of the triangle whose vertices are (2, −4), (−3, −7) and (7, 2)
Find the centroid of the triangle whose vertices are (−5, −5), (1, −4) and (−4, −2)
If the centroid of a triangle is at (4, −2) and two of its vertices are (3, −2) and (5, 2) then find the third vertex of the triangle
Find the length of median through A of a triangle whose vertices are A(−1, 3), B(1, −1) and C(5, 1)
The vertices of a triangle are (1, 2), (h, −3) and (−4, k). If the centroid of the triangle is at the point (5, −1) then find the value of `sqrt(("h" + "k")^2 + ("h" + 3"k")^2`
Orthocentre and centroid of a triangle are A(−3, 5) and B(3, 3) respectively. If C is the circumcentre and AC is the diameter of this circle, then find the radius of the circle
ABC is a triangle whose vertices are A(3, 4), B(−2, −1) and C(5, 3). If G is the centroid and BDCG is a parallelogram then find the coordinates of the vertex D.
If `(3/2, 5), (7, (-9)/2)` and `(13/2, (-13)/2)` are mid-points of the sides of a triangle, then find the centroid of the triangle
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board 5 Coordinate Geometry Exercise 5.6 [Pages 218 - 219]
Multiple Choice Questions
If the y-coordinate of a point is zero, then the point always lies ______
in the I quadrant
in the II quadrant
on x-axis
on y-axis
The points (−5, 2) and (2, −5) lie in the ________
same quadrant
II and III quadrant respectively
II and IV quadrant respectively
IV and II quadrant respectively
On plotting the points O(0, 0), A(3, 0), B(3, 4), C(0, 4) and joining OA, AB, BC and CO which of the following figure is obtained?
Square
Rectangle
Trapezium
Rhombus
If P(−1, 1), Q(3, −4), R(1, −1), S(−2, −3) and T(−4, 4) are plotted on a graph paper, then the points in the fourth quadrant are __________
P and T
Q and R
only S
P and Q
The point whose ordinate is 4 and which lies on the y-axis is _______________
(4, 0)
(0, 4)
(1, 4)
(4, 2)
The distance between the two points (2, 3) and (1, 4) is ______
2
`sqrt(56)`
`sqrt(10)`
`sqrt(2)`
If the points A(2, 0), B(– 6, 0), C(3, a – 3) lie on the x-axis then the value of a is _____
0
2
3
– 6
If (x + 2, 4) = (5, y – 2), then the coordinates (x, y) are _____
(7, 12)
(6, 3)
(3, 6)
(2, 1)
If Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4 are the quadrants in a Cartesian plane then Q2 ∩ Q3 is ___________
Q1 U Q2
Q2 U Q3
Null set
Negative x-axis
The distance between the point (5, −1) and the origin is _________
`sqrt(24)`
`sqrt(37)`
`sqrt(26)`
`sqrt(17)`
The coordinates of the point C dividing the line segment joining the points P(2, 4) and Q(5, 7) internally in the ratio 2 : 1 is
`(7/2, 11/2)`
(3, 5)
(4, 4)
(4, 6)
If `"P"("a"/3, "b"/2)` is the mid-point of the line segment joining A(−4, 3) and B(−2, 4) then (a, b) is
(−9, 7)
`(-3, 7/2)`
(9, −7)
`(3, -7/2)`
In what ratio does the point Q(1, 6) divide the line segment joining the points P(2, 7) and R(−2, 3)
1 : 2
2 : 1
1 : 3
3 : 1
If the coordinates of one end of a diameter of a circle is (3, 4) and the coordinates of its centre is (−3, 2), then the coordinate of the other end of the diameter is
(0, −3)
(0, 9)
(3, 0)
(−9, 0)
The ratio in which the x-axis divides the line segment joining the points A (a1, b1) and B (a2, b2) is
b1 : b2
−b1 : b2
a1 : a2
−a1 : a2
The ratio in which the x-axis divides the line segment joining the points (6, 4) and (1, −7) is
2 : 3
3 : 4
4 : 7
4 : 3
If the coordinates of the mid-points of the sides AB, BC and CA of a triangle are (3, 4), (1, 1) and (2, −3) respectively, then the vertices A and B of the triangle are
(3, 2), (2, 4)
(4, 0), (2, 8)
(3, 4), (2, 0)
(4, 3), (2, 4)
The mid-point of the line joining (−a, 2b) and (−3a, −4b) is
(2a, 3b)
(−2a, −b)
(2a, b)
(−2a, −3b)
In what ratio does the y-axis divides the line joining the points (−5, 1) and (2, 3) internally
1 : 3
2 : 5
3 : 1
5 : 2
If (1, −2), (3, 6), (x, 10) and (3, 2) are the vertices of the parallelogram taken in order, then the value of x is
6
5
4
3
Solutions for 5: Coordinate Geometry
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board chapter 5 - Coordinate Geometry Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board chapter 5 - Coordinate Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board chapter 5 - Coordinate Geometry
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 5 (Coordinate Geometry) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board chapter 5 Coordinate Geometry are Concept for Mapping the Space Around Approximately Through Visual Estimation., Plotting a Point in the Plane If Its Coordinates Are Given., Cartesian Coordinate System, Co-ordinates of Points and Distance, The Mid-point of a Line Segment (Mid-point Formula), Points of Trisection of a Line Segment (Mid-point Formula), Section Formula, The Coordinates of the Centroid.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board solutions Coordinate Geometry exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Coordinate Geometry Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
