Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
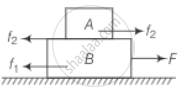
In Figure, the co-efficient of friction between the floor and the body B is 0.1. The co-efficient of friction between the bodies B and A is 0.2. A force F is applied as shown on B. The mass of A is m /2 and of B is m. Which of the following statements are true?

- The bodies will move together if F = 0.25 mg.
- The body A will slip with respect to B if F = 0.5 mg.
- The bodies will move together if F = 0.5 mg.
- The bodies will be at rest if F = 0.1 mg.
- The maximum value of F for which the two bodies will move together is 0.45 mg.
Solution
a, b, d and e
Explanation:
Consider the adjacent diagram. The frictional force on B(f1) and frictional force on A (f2) will be as shown.
Lat A and B are moving together `a_"common" = (F- t_1)/(m_A + m_B)`
= `(F - f_1)/((m/2) + m)`
= `(2(F - f_1))/(3 m)`
Pseudo force on `A = (m_A) xx a_"common"`
= `m_A xx (2(F - f_1))/(3m)`
= `m/2 xx (2(F - f_1))/(3m)`
= `(F - f_1))/3`
The force (F) will be maximum when
Pseudo force on A = Frictional force on A
⇒ `(F_"max" - f_1)/3 = μ m_A g`
= `0.2 xx m/2 xx g`
= 0.1 mg
⇒ `F_"max" = 0.3 mg + f_1`
= `0.3 mg + (0.1) 3/2 mg`
= 0.45 mg
⇒ Hence, the maximum force up to which bodies are together is `F_"max" = 0.45 mg`
a. Hence, for F = 0.25 mg < Fmax bodies will move together.
b. For F = 0.5 mg > Fmax, body A will slip with respect to B.
c. For F = 0.5 mg > Fmax, bodies slip.
`(f_1)_"max" = μ m_Bg = (0.1) xx 3/2 m xx g` = 0.15 mg
`(f_2)_"max" = μ m_Ag = (0.2) (m/g) g` = 0.1 mg
Hence, the minimum force required for moment of the system (A + B)
`F_"min" = (f_1)_"max" + (f_2)_"max"`
= 0.15 mg + 0.1 mg
= 0.25 mg
d. Given, force F = 0.1 mg < Fmin.
Hence, the bodies will be at rest.
e. Maximum force for combined movement Fmax = 0.45 mg.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
One end of a string of length l is connected to a particle of mass m and the other to a small peg on a smooth horizontal table. If the particle moves in a circle with speed the net force on the particle (directed towards the centre) is:
T is the tension in the string.
A body of mass 5 kg is acted upon by two perpendicular forces 8 N and 6 N. Give the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the body.
A truck starts from rest and accelerates uniformly at 2.0 m s–2. At t = 10 s, a stone is dropped by a person standing on the top of the truck (6 m high from the ground).
- What are the velocity, and
- acceleration of the stone at t = 11?(Neglect air resistance.)
Explain why a horse cannot pull a cart and run in empty space.
Mass m1 moves on a slope making an angle θ with the horizontal and is attached to mass m2 by a string passing over a frictionless pulley as shown in figure. The coefficient of friction between m1 and the sloping surface is µ.

- If m2 > m1 sin θ, the body will move up the plane.
- If m2 > m1 (sin θ + µ cos θ), the body will move up the plane.
- If m2 < m1 (sin θ + µ cos θ), the body will move up the plane.
- If m2 < m1 (sin θ − µ cos θ), the body will move down the plane.
Why are mountain roads generally made winding upwards rather than going straight up?
Two masses of 5 kg and 3 kg are suspended with help of massless inextensible strings as shown in figure. Calculate T1 and T2 when whole system is going upwards with acceleration = 2 ms2 (use g = 9.8 ms–2).

A block of mass M is held against a rough vertical wall by pressing it with a finger. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is µ and the acceleration due to gravity is g, calculate the minimum force required to be applied by the finger to hold the block against the wall?
A person in an elevator accelerating upwards with an acceleration of 2 ms–2, tosses a coin vertically upwards with a speed of 20 ms1. After how much time will the coin fall back into his hand? ( g = 10 ms–2)
A rectangular box lies on a rough inclined surface. The co-efficient of friction between the surface and the box is µ. Let the mass of the box be m.
- At what angle of inclination θ of the plane to the horizontal will the box just start to slide down the plane?
- What is the force acting on the box down the plane, if the angle of inclination of the plane is increased to α > θ ?
- What is the force needed to be applied upwards along the plane to make the box either remain stationary or just move up with uniform speed?
- What is the force needed to be applied upwards along the plane to make the box move up the plane with acceleration a?
