Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In parallelogram PQRS, ∠Q = (4x – 5)° and ∠S = (3x + 10)°. Calculate: ∠Q and ∠R.
Solution
In parallelogram PQRS,
∠Q = (4x – 5)° and ∠S = (3x + 10)°
opposite ∠s of //gm are equal.
∠Q = ∠S
4x – 5 = 3x + 10
4x – 3x = 10+5
x = 15
∠Q = 4x – 5 =4 x 15 – 5 = 55°
Also ∠Q + ∠R = 180°
55° + ∠R = 180°
∠R = 180°–55° = 125°
∠Q = 55° ; ∠R = 125°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can a quadrilateral ABCD be a parallelogram if AB = DC = 8 cm, AD = 4 cm and BC = 4.4 cm?
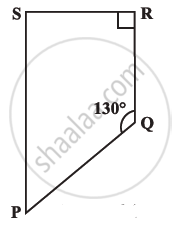
Find the measure of ∠P and ∠S, if `bar(SP) || bar(RQ)` in the following figure. (If you find m∠R, is there more than one method to find m∠P?).
Ratio of two adjacent sides of a parallelogram is 3 : 4, and its perimeter is 112 cm. Find the length of its each side.
ABCD is a parallelogram. What kind of quadrilateral is it if: AC is perpendicular to BD but is not equal to it?
Prove that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Which of the following figures satisfy the following properties?
- All sides are congruent.
- All angles are right angles.
- Opposite sides are parallel.
Which of the following is a property of a parallelogram?
Two angles of a quadrilateral are each of measure 75° and the other two angles are equal. What is the measure of these two angles? Name the possible figures so formed.
Construct a parallelogram ABCD in which AB = 4 cm, BC = 5 cm and ∠B = 60°.
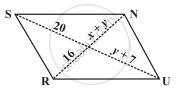
The following figure RUNS is parallelogram. Find x and y. (Lengths are in cm)