Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In parallelogram PQRS, ∠Q = (4x – 5)° and ∠S = (3x + 10)°. Calculate: ∠Q and ∠R.
उत्तर
In parallelogram PQRS,
∠Q = (4x – 5)° and ∠S = (3x + 10)°
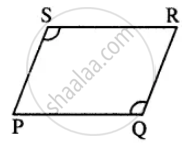
opposite ∠s of //gm are equal.
∠Q = ∠S
4x – 5 = 3x + 10
4x – 3x = 10+5
x = 15
∠Q = 4x – 5 =4 x 15 – 5 = 55°
Also ∠Q + ∠R = 180°
55° + ∠R = 180°
∠R = 180°–55° = 125°
∠Q = 55° ; ∠R = 125°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Can a quadrilateral ABCD be a parallelogram if ∠D + ∠B = 180°?
Can a quadrilateral ABCD be a parallelogram if ∠A = 70° and ∠C = 65°?
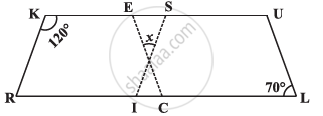
In the above figure both RISK and CLUE are parallelograms. Find the value of x.
If the ratio of measures of two adjacent angles of a parallelogram is 1 : 2, find the measures of all angles of the parallelogram.
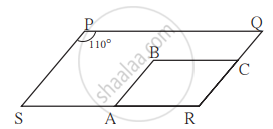
In the given figure, `square`PQRS and `square`ABCR are two parallelograms. If ∠P = 110° then find the measures of all angles of `square`ABCR.
Ratio of consecutive angles of a quadrilateral is 1 : 2 : 3 : 4. Find the measure of its each angle. Write, with reason, what type of a quadrilateral it is.
Given: Parallelogram ABCD in which diagonals AC and BD intersect at M.
Prove: M is the mid-point of LN.
In parallelogram ABCD, E is the mid-point of side AB and CE bisects angle BCD. Prove that :
(i) AE = AD,
(ii) DE bisects and ∠ADC and
(iii) Angle DEC is a right angle.
If two adjacent angles of a parallelogram are (5x – 5)° and (10x + 35)°, then the ratio of these angles is ______.
The angle between the two altitudes of a parallelogram through the vertex of an obtuse angle of the parallelogram is 45°. Find the angles of the parallelogram.
