Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In parallelogram ABCD, ∠A = 3 times ∠B. Find all the angles of the parallelogram. In the same parallelogram, if AB = 5x – 7 and CD = 3x +1 ; find the length of CD.
उत्तर
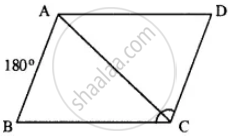
Let ∠B = x
∠A = 3 ∠B = 3x
AD || BC
∠A + ∠B = 180°
3x + x = 180°
⇒ 4x = 180°
⇒ x = 45°
∠B = 45°
∠A = 3x = 3 x 45 = 135°
and ∠B = ∠D = 45°
opposite angles of || gm are equal.
∠A = ∠C = 135°
opposite sides of //gm are equal.
AB = CD
5x – 7 = 3x + 1
⇒ 5x – 3x = 1+7
⇒ 2x = 8
⇒ x = 4
CD = 3 x 4+1 = 13
Hence 135°, 45°, 135° and 45° ; 13
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
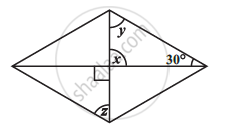
Consider the given parallelograms. Find the values of the unknowns x, y, z.
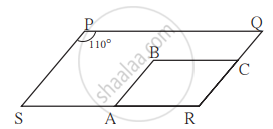
In the given figure, `square`PQRS and `square`ABCR are two parallelograms. If ∠P = 110° then find the measures of all angles of `square`ABCR.
In the adjacent figure, if seg AB || seg PQ, seg AB ≅ seg PQ, seg AC || seg PR, seg AC ≅ seg PR then prove that, seg BC || seg QR and seg BC ≅ seg QR.
Prove that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
In parallelogram ABCD, E is the mid-point of AD and F is the mid-point of BC. Prove that BFDE is a parallelogram.
The given figure shows parallelogram ABCD. Points M and N lie in diagonal BD such that DM = BN.
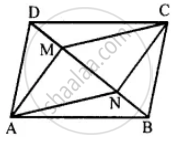
Prove that:
(i) ∆DMC = ∆BNA and so CM = AN
(ii) ∆AMD = ∆CNB and so AM CN
(iii) ANCM is a parallelogram.
A diagonal of a parallelogram bisects an angle. Will it also bisect the other angle? Give reason.
The angle between the two altitudes of a parallelogram through the vertex of an obtuse angle of the parallelogram is 45°. Find the angles of the parallelogram.
ABCD is a parallelogram. Points P and Q are taken on the sides AB and AD respectively and the parallelogram PRQA is formed. If ∠C = 45°, find ∠R.
Draw a rough figure of a quadrilateral that is not a parallelogram but has exactly two opposite angles of equal measure.
