Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Ratio of consecutive angles of a quadrilateral is 1 : 2 : 3 : 4. Find the measure of its each angle. Write, with reason, what type of a quadrilateral it is.
उत्तर
Suppose PQRS is a quadrilateral.
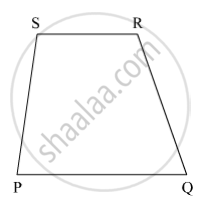
Let m∠P : m∠Q : m∠R : m∠S = 1 : 2 : 3 : 4
So, m∠P = k, m∠Q = 2k, m∠R = 3k and m∠S = 4k, where k is some constant
Now,
m∠P + m∠Q + m∠R + m∠S = 360°
∴ k + 2k + 3k + 4k = 360°
⇒ 10k = 360°
⇒ k = 36°
∴ m∠P = 36°
m∠Q = 2k = 2 × 36° = 72°
m∠R = 3k = 3 × 36° = 108°
m∠S = 4k = 4 × 36° = 144°
Now, m∠P + m∠S = 36° + 144° = 180°
We know if two lines are intersected by a transversal such that the sum of interior angles on the same transversal is supplementary, then the two lines are parallel.
∴ Side PQ || Side SR
Also, m∠P + m∠Q = 36° + 72° = 108° ≠ 180°
So, side PS is not parallel to side QR.
In quadrilateral PQRS, only one pair of opposite sides is parallel. Therefore, quadrilateral PQRS is a trapezium.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider the given parallelogram. Find the values of the unknowns x, y, z.

Consider the given parallelogram. Find the values of the unknowns x, y, z.
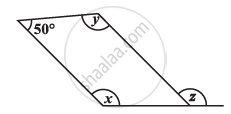
Use the information given in the alongside diagram to find the value of x, y, and z.
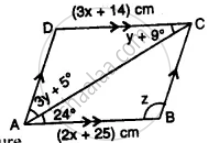
If two adjacent angles of a parallelogram are (5x – 5)° and (10x + 35)°, then the ratio of these angles is ______.
The angle between the two altitudes of a parallelogram through the same vertex of an obtuse angle of the parallelogram is 30°. The measure of the obtuse angle is ______.
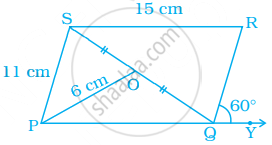
In parallelogram PQRS, O is the mid point of SQ. Find ∠S, ∠R, PQ, QR and diagonal PR.
In parallelogram MODE, the bisector of ∠M and ∠O meet at Q, find the measure of ∠MQO.
In the following figure of a ship, ABDH and CEFG are two parallelograms. Find the value of x.
In parallelogram ABCD, the angle bisector of ∠A bisects BC. Will angle bisector of B also bisect AD? Give reason.
Construct a parallelogram when one of its side is 4 cm and its two diagonals are 5.6 cm and 7 cm. Measure the other side.
