Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the study of a photoelectric effect the graph between the stopping potential V and frequency v of the incident radiation on two different metals P and Q is shown below:

(i) Which one of the two metals has higher threshold frequency?
(ii) Determine the work function of the metal which has greater value.
(iii) Find the maximum kinetic energy of electron emitted by light of frequency 8 × 1014 Hz for this metal.
Solution
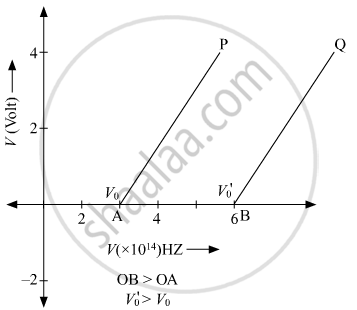
So the threshold frequency of metal Q is greater than metal P.
(ii)
Work function, w0=hν0
where, v0 is threshold frequency.
(ν0)Q>(ν0)P
⇒WQ>WP
(iii) Maximum kinetic energy is given by
K=E−hν0
WQ>WP
Hence the kinetic energy for metal Q is
E=hν−hν0
= h(v−v0)
=6.63×10−34×(8×1014−6×1014)
=1.33×10−19 J
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The amplitude of the magnetic field part of a harmonic electromagnetic wave in vacuum is B0 = 510 nT. What is the amplitude of the electric field part of the wave?
Do electromagnetic waves carry energy and momentum ?
Which mode of propagation is used by short wave broadcast serves?
What are the directions of electric and magnetic field vectors relative to each other and relative to the direction of propagation of electromagnetic waves?
Write the following radiations in ascending order with respect to their frequencies:
X-rays, microwaves, UV rays and radio waves.
A capacitor is connected to an alternating-current source. Is there a magnetic field between the plates?
What are Fraunhofer lines? How are they useful in the identification of elements present in the Sun?
Write a short note on the radio waves.
Let an electromagnetic wave propagate along the x-direction, the magnetic field oscillates at a frequency of 1010 Hz and has an amplitude of 10-5 T, acting along the y – direction. Then, compute the wavelength of the wave. Also write down the expression for the electric field in this case.
An EM wave of intensity I falls on a surface kept in vacuum and exerts radiation pressure p on it. Which of the following are true?
- Radiation pressure is `I/c` if the wave is totally absorbed.
- Radiation pressure is `I/c` if the wave is totally reflected.
- Radiation pressure is `(2I)/c` if the wave is totally reflected.
- Radiation pressure is in the range `I/c < p < (2I)/c` for real surfaces.
