Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given diagram, ΔABC ∼ ΔPQR. If AD and PS are bisectors of ∠BAC and ∠QPR respectively then ______.
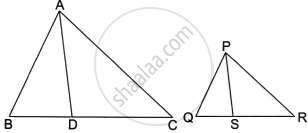
Options
ΔABC ∼ ΔPQS
ΔABD ∼ ΔPQS
ΔABD ∼ ΔPSR
ΔABC ∼ ΔPSR
MCQ
Fill in the Blanks
Solution
In the given diagram, ΔABC ∼ ΔPQR. If AD and PS are bisectors of ∠BAC and ∠QPR respectively then ΔABD ∼ ΔPQS.
Explanation:

Here, ΔABC ∼ ΔPQR
∴ ∠A = ∠P
Then, `1/2 ∠A = 1/2 ∠P` or ∠BAD = ∠QPS ...(i)
And ∠B = ∠Q ...(ii)
In ΔABD and ΔPQS,
∠BAD = ∠QPS ...[From (i)]
∠B = ∠Q ...[From (ii)]
Then, ΔABD ∼ ΔPQS ...(By AA similarity criterion)
shaalaa.com
Conditions for Similarity of Two Triangles: (Sas, Aa Or Aaa and Sss)
Is there an error in this question or solution?
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
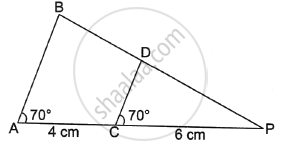
In the given figure ∠BAP = ∠DCP = 70°, PC = 6 cm and CA = 4 cm, then PD : DB is ______.
In the given diagram ΔADB and ΔACB are two right angled triangles with ∠ADB = ∠BCA = 90°. If AB = 10 cm, AD = 6 cm, BC = 2.4 cm and DP = 4.5 cm.
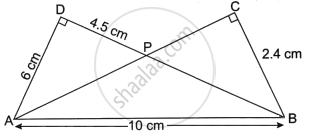
- Prove that ΔAPD ∼ ΔBPC
- Find the length of BD and PB
- Hence, find the length of PA
- Find area ΔAPD : area ΔBPC.
