Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given diagram ΔADB and ΔACB are two right angled triangles with ∠ADB = ∠BCA = 90°. If AB = 10 cm, AD = 6 cm, BC = 2.4 cm and DP = 4.5 cm.
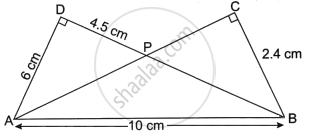
- Prove that ΔAPD ∼ ΔBPC
- Find the length of BD and PB
- Hence, find the length of PA
- Find area ΔAPD : area ΔBPC.
Solution
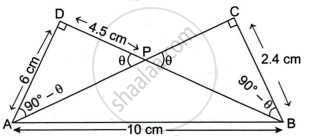
Given: In ΔADB and ΔACB,
∠ADB = ∠BCA = 90°
AB = 10 cm, AD = 6 cm, BC = 2.4 cm, DP = 4.5 cm
a. In ΔAPD and ΔBPC
∠APD = ∠BPC ...(Vertically opposite angles)
∠ADP = ∠BCP = 90°
∴ ΔAPD ∼ ΔBCP ...(By AA similarity criterion)
b. In ΔABD,
By pythagoras theorem,
AB2 = AD2 + BD2
(10)2 = 62 + (BD)2
BD2 = 100 – 36 = 64
BD = 8 cm
Then, PB = BD – PD
= 8 – 4.5
= 3.5 cm
c. In ΔPAD,
By pythagoras theorem,
AP2 = AD2 + PD2
AP2 = 62 + (4.5)2
= 36 + 20.25
= 56.25
AP = `sqrt(56.25)` cm
AP = 7.5 cm
d. Since, ΔAPD ∼ ΔBPC
∴ `(ar(ΔAPD))/(ar(ΔBPC)) = (AD^2)/(BC^2)`
= `(6 xx 6)/(2.4 xx 2.4)`
= `(1 xx 1)/(0.4 xx 0.4)`
= `(10 xx 10)/(4 xx 4)`
= `25/4`
Hence, ar(ΔAPD) : ar(ΔBPC) = 25 : 4