Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Observe the figure below. Write functions of the labelled parts.

Solution
- Gynoecium (Carpel): It is an essential whorl. It is consists of stigma, style and ovary. It acts as a female reproductive part of the flower. It is responsible for the production of female gametes.
- Androecium (Stamen): It is an essential whorl. It is consists of anther and filament. It acts as a male reproductive part of the flower. It is responsible for the production of male gametes.
- Calyx and corolla: Calyx and corolla are accessory whorls. They are responsible for the protection of inner (essential) whorls.
- Pedicel: Pedicel is a small stalk which supports the flower.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
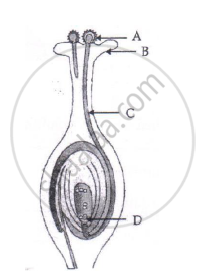
(i) Name the part marked 'A' in the diagram.
(ii) How dose 'A' reachese part 'B'?
(iii) State the importance of the part 'C'.
(iv) What happens to the part marked 'D' after fertilisation is over?
A student has to perform the experiment "To identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed." Select from the following an appropriate group of seeds:
(a) Pea, gram, wheat
(b) Red kidney bean, maize, gram
(c) Maize, wheat, red kidney bean
(d) Red kidney bean, pea, gram
Answer the following question.
State significance of pollination.
Give one example of a unisexual flower.
A flower may have either male or female reproductive parts. Such a flower is called ______.
How does the process of fertilisation take place in flowers?
The process of fusion of the male and female gametes is called ______.
State the name of the functional unit concerned with sexual reproduction.
Name the male part of the flower.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
Pollen grains contain ............ gametes of a plant.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The ovule becomes a .......... after fertilisation.
How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
In tobacco plant, the male gametes have 24 chromosomes.
What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete?
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events of sexual reproduction in a flower?
(a) pollination, fertilisation, seed, embryo
(b) seed, embryo, fertilisation, pollination
(c) pollination, fertilisation, embryo, seed
(d) embryo, seed, pollination, fertilisation
The length of pollen tube depends on the distance between :
(a) pollen grain and upper surface of stigma
(b) pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
(c) pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
(d) upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
In a bisexual flower, inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Explain.
In what ways is fertilisation in a plant similar to fertilisation in a human?
Multiple choice question. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
The male gamete is present inside the which germinates.
- the style
- the stigma
- the anther
- the ovary
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F):
Flowers which possess stamens and carpel are called unisexual.
Draw a labelled diagram of a bisexual flower.
Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram and write their names.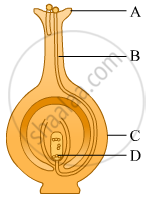
A student is asked to study the different parts of an embryo of pea seeds. Given below are the essential steps for the experiment :
(I) Soak the pea seeds in plain water and keep them overnight.
(II) Cut open the soaked seed and observe its different parts.
(III) Take some pea seeds in a petri dish.
(IV) Drain the excess water. Cover the seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them as it is for a day.
The correct sequence of these steps is
(A) III, I, IV, II
(B) III, IV, I, II
(C) III, I, II, IV
(D) III, II, I, IV
In the figure, the parts marked A, B and C are sequentially:

(A) Plumule, Radicle and Cotyledon
(B) Radicle, Plumule and Cotyledon
(C) Plumule, Cotyledon and Radicle
(D) Radicle, Cotyledon and Plumule
Distinguish between unisexual and bisexual flowers giving one example of each. Draw a diagram showing process of germination of pollen grains on stigma and label the following parts:
(a) Female germ cell
(b) Male germ cell
(c) Ovary
What is phototropism?
List any two differences between pollination and fertilisation.
Find the odd one out:
__________ is present in unisexual flower.
What does germination mean?
The essential parts of a flower are ______.
Which of the following is the outermost protective layer of anther?
Which type of development is observed in male gametophytes of plants?
Identify the female gametophyte in angiosperms.
Gloriosa superba exhibits ______.
In a bisexual flower inspite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Provide a suitable explanation for the above situation.
Give reason for the following:
Fertilization cannot take place in flowers if pollination does not occur.
Sketch and label the essential and accessory whorls of flower.
What are the agents for pollination?
The figure below shows the concept of double fertilization. Complete the flow chart showing the progress at each step:

Type of sexual reproduction is ______.
