Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
One zero of the polynomial `3x^3+16x^2 +15x-18 is 2/3` . Find the other zeros of the polynomial.
Solution
Given: `x =2/3` is one of the zero of` 3x^3 + 16x^2 + 15x – 18`
Now, we have
`x=2/3`
`⇒ x-2/3=0`
Now, we divide `3x^3 + 16x^2 + 15x – 18 by x –2/3` to find the quotient 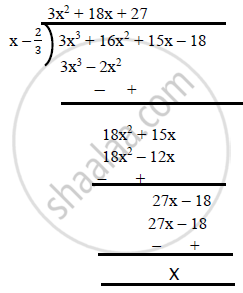
So, the quotient is `3x^2+18x+27`
Now,
`3x^2 + 18x + 27 = 0`
⇒ `3x^2 + 9x + 9x + 27 = 0`
⇒ `3x(x + 3) + 9(x + 3) = 0`
⇒ (x + 3) (3x + 9) = 0
⇒ (x + 3) = 0 or (3x + 9) = 0
⇒ x = –3 or x = –3
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
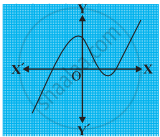
The graphs of y = p(x) are given in following figure, for some polynomials p(x). Find the number of zeroes of p(x).
Obtain all other zeroes of `(x^4 + 4x^3 – 2x^2 – 20x – 15)` if two of its zeroes are `sqrt5 and –sqrt5.`
If -2 is a zero of the polynomial `3x^2 + 4x + 2k` then find the value of k.
If the sum of the zeros of the quadratic polynomial `kx^2-3x + 5` is 1 write the value of k..
If 𝛼 and 𝛽 be the zeroes of the polynomial `2x^2 - 7x + k` write the value of (𝛼 + 𝛽+ 𝛼 𝛽.
Find the sum of the zeros and the product of zeros of a quadratic polynomial, are `−1/2` and \ -3 respectively. Write the polynomial.
A quadratic polynomial, whose zeroes are -3 and 4, is ______.
10. The zeroes of the quadratic polynomial x² + kx + k, k? 0.
If 4x² – 6x – m is divisible by x – 3, the value of m is exact divisor of ______.
If the graph of a polynomial intersects the x-axis at exactly two points, it need not be a quadratic polynomial.
