Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
Options
\[\frac{1}{T}\]
\[\sqrt{T}\]
T
T2
Solution
T
Root mean squared velocity is given by\[v_{rms} = \sqrt{\frac{3RT}{M}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( v_{rms} \right)^2 = \frac{3RT}{M}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( v_{rms} \right)^2 \alpha T\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When we place a gas cylinder on a van and the van moves, does the kinetic energy of the molecules increase? Does the temperature increase?
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey an additional law pV2 = constant. The gas is initially at a temperature T and volume V. Find the temperature when it expands to a volume 2V.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
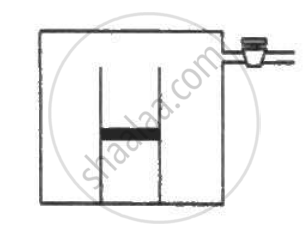
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 10 cm2 and weight 1 kg in figure. The vessel itself is kept in a big chamber containing air at atmospheric pressure 100 kPa. The length of the gas column is 20 cm. If the chamber is now completely evacuated by an exhaust pump, what will be the length of the gas column? Assume the temperature to remain constant throughout the process.
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
The temperature and the dew point in an open room are 20°C and 10°C. If the room temperature drops to 15°C, what will be the new dew point?
Answer in brief:
What will happen to the mean square speed of the molecules of a gas if the temperature of the gas increases?
If the density of oxygen is 1.44 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 N/m2, find the root mean square velocity of oxygen molecules.
The number of degrees of freedom, for the vibrational motion of a polyatomic molecule, depends on the ______
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
A ring of mass m and radius r rotates about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with angular velocity `omega`. Its kinetic energy is ______.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas is 'E1'. The kinetic energy of the electron (e) accelerated from rest through p.d. 'V' volt is 'E2'. The temperature at which E1 = E2 is possible, is ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
23Ne decays to 23Na by negative beta emission. Mass of 23Ne is 22.994465 amu mass of 23Na is 22.989768 amu. The maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons neglecting the kinetic energy of recoiling product nucleus is ______ MeV.
A proton, a deuteron and an α-particle with same kinetic energy enter into a uniform magnetic field at right angle to magnetic field. The ratio of the radii of their respective circular paths is ______.
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
Assuming the expression for the pressure P exerted by an ideal gas, prove that the kinetic energy per unit volume of the gas is `3/2` P.
