Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The temperature and the dew point in an open room are 20°C and 10°C. If the room temperature drops to 15°C, what will be the new dew point?
Solution
Here ,
Temperature = `20^circ`C
Dew Point = `10^circ`C
Air becomes saturated at `10^circ`C . But if the room temperature is lowered to `15^circ`C , the Dew point will still be at `10^circ`C .
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey an additional law pV2 = constant. The gas is initially at a temperature T and volume V. Find the temperature when it expands to a volume 2V.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process `P = (P_0)/(1+(V/V_0)^2` where `p_0` and `V_0` are constants . Find the temperature of the gas when `V=V_0` .
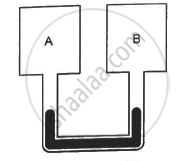
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
Answer in brief:
What will happen to the mean square speed of the molecules of a gas if the temperature of the gas increases?
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Answer in brief:
Compare the rms speed of hydrogen molecules at 127ºC with rms speed of oxygen molecules at 27ºC given that molecular masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 2 and 32 respectively.
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
Under which condition laws of Boyle, Charles, and Gay-Lussac are valid?
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
Above what temperature, all bodies radiate electromagnetic radiation?
A metal cube of length 4 cm radiates heat at the rate of 10 J/s. Find its emissive power at a given temperature.
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
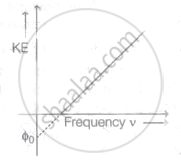
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
Assuming the expression for the pressure P exerted by an ideal gas, prove that the kinetic energy per unit volume of the gas is `3/2` P.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
