Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
Solution
All bodies radiate as well as absorb radiation at room temperature, but their rate of emission and rate of absorption is the same, hence their temperature remains constant.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Consider a gas of neutrons. Do you expect it to behave much better as an ideal gas as compared to hydrogen gas at the same pressure and temperature?
If the molecules were not allowed to collide among themselves, would you expect more evaporation or less evaporation?
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
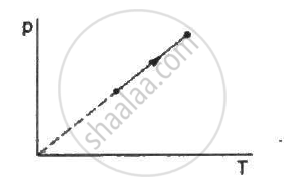
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
0.040 g of He is kept in a closed container initially at 100.0°C. The container is now heated. Neglecting the expansion of the container, calculate the temperature at which the internal energy is increased by 12 J.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
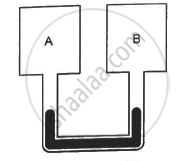
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
Answer in brief:
Show that rms velocity of an oxygen molecule is `sqrt2` times that of a sulfur dioxide molecule at S.T.P.
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
Earth’s mean temperature can be assumed to be 280 K. How will the curve of blackbody radiation look like for this temperature? Find out λmax. In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum, does this value lie? (Take Wien's constant b = 2.897 × 10−3 m K)
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
Under which condition laws of Boyle, Charles, and Gay-Lussac are valid?
What is the microscopic origin of temperature?
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
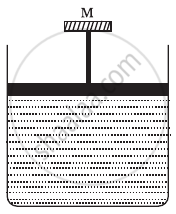
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity vo. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
The Q-value of a nuclear reaction and kinetic energy of the projectile particle, KP are related as ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and t = 0.04, then the value of r is ______.
Show that the average energy per molecule is proportional to the absolute temperature T of the gas.
2000 calories of radiant heat is incident on a body. If the body absorbs 550 calories of heat, find the coefficient of emmission of the body.
