Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
Solution
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
Kinetic energy per mole of an ideal gas is directly proportional to T. So, it will be the same for all ideal gases.
Number of molecules in 1 mole of an ideal is the same for all ideal gases because ideal gases obey Avogadro's law.
Thus, (a) and (c) are correct answers.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
0.040 g of He is kept in a closed container initially at 100.0°C. The container is now heated. Neglecting the expansion of the container, calculate the temperature at which the internal energy is increased by 12 J.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
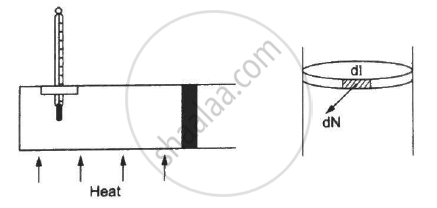
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
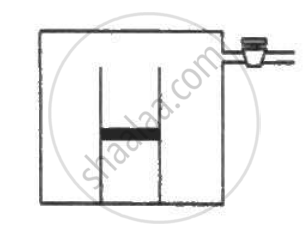
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 10 cm2 and weight 1 kg in figure. The vessel itself is kept in a big chamber containing air at atmospheric pressure 100 kPa. The length of the gas column is 20 cm. If the chamber is now completely evacuated by an exhaust pump, what will be the length of the gas column? Assume the temperature to remain constant throughout the process.
The temperature and the dew point in an open room are 20°C and 10°C. If the room temperature drops to 15°C, what will be the new dew point?
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Answer in brief:
Compare the rms speed of hydrogen molecules at 127ºC with rms speed of oxygen molecules at 27ºC given that molecular masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 2 and 32 respectively.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
Above what temperature, all bodies radiate electromagnetic radiation?
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity vo. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
For a particle moving in vertical circle, the total energy at different positions along the path ______.
According to the kinetic theory of gases, at a given temperature, molecules of all gases have the same ______.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
