Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
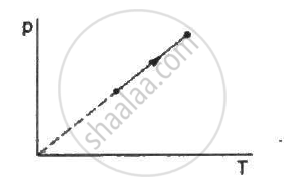
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
Options
isothermal
isobaric
isochoric
none of these
Solution
isochoric
According to the graph, P is directly proportional to T.
Applying the equation of state, we get
PV = nRT
\[\Rightarrow P = \frac{nR}{V}T\]
\[\text { Given : } P \alpha T\]
\[\text { This means }\frac{nR}{V} \text { is a constant . So, V is also a constant }.\]
Constant V implies the process is isochoric.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey an additional law pV2 = constant. The gas is initially at a temperature T and volume V. Find the temperature when it expands to a volume 2V.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area A fitted with two frictionless pistons. The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire. Initially, the temperature of the gas is T0 and its pressure is p0 which equals the atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the tension in the wire? (b) What will be the tension if the temperature is increased to 2T0 ?

If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
Answer in brief:
Show that rms velocity of an oxygen molecule is `sqrt2` times that of a sulfur dioxide molecule at S.T.P.
If the density of oxygen is 1.44 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 N/m2, find the root mean square velocity of oxygen molecules.
Earth’s mean temperature can be assumed to be 280 K. How will the curve of blackbody radiation look like for this temperature? Find out λmax. In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum, does this value lie? (Take Wien's constant b = 2.897 × 10−3 m K)
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
The average translational kinetic energy of gas molecules depends on ____________.
What is the microscopic origin of temperature?
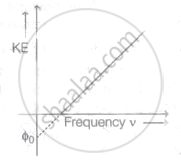
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9 × 10 6 ms−1 and 1 × 106 ms−1, respectively. What is the root mean square speed of these molecules?
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and t = 0.04, then the value of r is ______.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
