Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
Options
0.02
0.04
0.4
0.2
Solution
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is 0.04.
Explanation:
Express the relation of absorptivity. The fraction of light/ray/radiation absorbed by a surface is called absorptivity.
`a = (G_(abs))/G`
`G_(abs) =Ga`
Here, `G_(abs)` is absorbed radiation and G is incident radiation.
Express the relation of reflectivity.
The fraction of light reflected by a surface is known as reflectivity.
`r = (G_(ref))/G`
`G_(ref) = Gr`
Here, `G_(ref)` is reflected radiation.
Express the relation of transmissivity. The fraction of light/ray/radiation transmitted by a surface is known as transmissivity.
`t_r = G_t/G`
`G_t = Gt_r`
Here, `G_t` is transmitted radiation.
Express the relation of 1st law of thermodynamics. Sum of all radiation (absorbed, reflected and transmitted) should be equals to the total radiation.
`G_(abs) + G_(ref) + G_t = G` ......(i)
Substitute `Ga` for `G_(abs), G_r` for `G_(mf)` and Gt for Gt in equation (i).
`(Ga)/G + (Gr)/G + (Gt_r)/G` = 1
`a + r + t_r` = 1
Substitute 0.72 for a and 0.24 for r to find transmitted radiation.
0.72 + 0.24 + tr = 1
tr = 1 – 0.96
tr = 0.04
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey an additional law pV2 = constant. The gas is initially at a temperature T and volume V. Find the temperature when it expands to a volume 2V.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
An ideal gas is trapped between a mercury column and the closed-end of a narrow vertical tube of uniform base containing the column. The upper end of the tube is open to the atmosphere. The atmospheric pressure equals 76 cm of mercury. The lengths of the mercury column and the trapped air column are 20 cm and 43 cm respectively. What will be the length of the air column when the tube is tilted slowly in a vertical plane through an angle of 60°? Assume the temperature to remain constant.
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
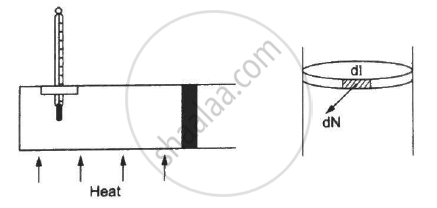
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area A fitted with two frictionless pistons. The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire. Initially, the temperature of the gas is T0 and its pressure is p0 which equals the atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the tension in the wire? (b) What will be the tension if the temperature is increased to 2T0 ?

The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
If the density of oxygen is 1.44 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 N/m2, find the root mean square velocity of oxygen molecules.
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
The emissive power of a sphere of area 0.02 m2 is 0.5 kcal s-1m-2. What is the amount of heat radiated by the spherical surface in 20 seconds?
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
When photons of energy hv fall on a metal plate of work function 'W0', photoelectrons of maximum kinetic energy 'K' are ejected. If the frequency of the radiation is doubled, the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected photoelectrons will be ______.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas is 'E1'. The kinetic energy of the electron (e) accelerated from rest through p.d. 'V' volt is 'E2'. The temperature at which E1 = E2 is possible, is ______.
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
Assuming the expression for the pressure P exerted by an ideal gas, prove that the kinetic energy per unit volume of the gas is `3/2` P.
At what temperature will therms velocity of a gas be four times its value at STP?
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
