Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
पर्याय
0.02
0.04
0.4
0.2
उत्तर
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is 0.04.
Explanation:
Express the relation of absorptivity. The fraction of light/ray/radiation absorbed by a surface is called absorptivity.
`a = (G_(abs))/G`
`G_(abs) =Ga`
Here, `G_(abs)` is absorbed radiation and G is incident radiation.
Express the relation of reflectivity.
The fraction of light reflected by a surface is known as reflectivity.
`r = (G_(ref))/G`
`G_(ref) = Gr`
Here, `G_(ref)` is reflected radiation.
Express the relation of transmissivity. The fraction of light/ray/radiation transmitted by a surface is known as transmissivity.
`t_r = G_t/G`
`G_t = Gt_r`
Here, `G_t` is transmitted radiation.
Express the relation of 1st law of thermodynamics. Sum of all radiation (absorbed, reflected and transmitted) should be equals to the total radiation.
`G_(abs) + G_(ref) + G_t = G` ......(i)
Substitute `Ga` for `G_(abs), G_r` for `G_(mf)` and Gt for Gt in equation (i).
`(Ga)/G + (Gr)/G + (Gt_r)/G` = 1
`a + r + t_r` = 1
Substitute 0.72 for a and 0.24 for r to find transmitted radiation.
0.72 + 0.24 + tr = 1
tr = 1 – 0.96
tr = 0.04
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
Consider a gas of neutrons. Do you expect it to behave much better as an ideal gas as compared to hydrogen gas at the same pressure and temperature?
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
The average translational kinetic energy of air molecules is 0.040 eV (1 eV = 1.6 × 10−19J). Calculate the temperature of the air. Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1.
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
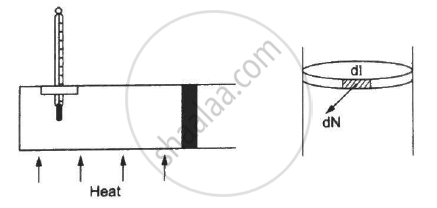
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
The temperature and the dew point in an open room are 20°C and 10°C. If the room temperature drops to 15°C, what will be the new dew point?
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

An adiabatic cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area 1 cm2 is closed at one end and fitted with a piston at the other end. The tube contains 0.03 g of an ideal gas. At 1 atm pressure and at the temperature of the surrounding, the length of the gas column is 40 cm. The piston is suddenly pulled out to double the length of the column. The pressure of the gas falls to 0.355 atm. Find the speed of sound in the gas at atmospheric temperature.
Answer in brief:
A gas in a cylinder is at pressure P. If the masses of all the molecules are made one-third of their original value and their speeds are doubled, then find the resultant pressure.
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Answer in brief:
Compare the rms speed of hydrogen molecules at 127ºC with rms speed of oxygen molecules at 27ºC given that molecular masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 2 and 32 respectively.
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
The emissive power of a sphere of area 0.02 m2 is 0.5 kcal s-1m-2. What is the amount of heat radiated by the spherical surface in 20 seconds?
Compare the rates of emission of heat by a blackbody maintained at 727°C and at 227°C, if the black bodies are surrounded by an enclosure (black) at 27°C. What would be the ratio of their rates of loss of heat?
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
What is the microscopic origin of temperature?
A ring of mass m and radius r rotates about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with angular velocity `omega`. Its kinetic energy is ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of average K.E.
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
A proton, a deuteron and an α-particle with same kinetic energy enter into a uniform magnetic field at right angle to magnetic field. The ratio of the radii of their respective circular paths is ______.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
