Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the microscopic origin of temperature?
उत्तर
The average K.E per molecule `bar"KE"` = ϵ = `3/2"kT"`
The equation implies that the temperature of a gas is a measure of the average translational K.E. per molecule of the gas.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
Find the number of molecules of an ideal gas in a volume of 1.000 cm3 at STP.
A glass contains some water at room temperature 20°C. Refrigerated water is added to it slowly. when the temperature of the glass reaches 10°C, small droplets condense on the outer surface. Calculate the relative humidity in the room. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 17.5 mm of mercury is 20°C and at 8.9 mm of mercury it is 10°C.
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Find the kinetic energy of 5 litres of a gas at STP, given the standard pressure is 1.013 × 105 N/m2.
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
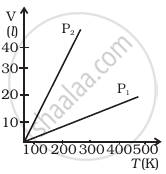
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity vo. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
