Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
उत्तर १
- At constant temperature, a gas's average kinetic energy per molecule remains constant.
- When a gas's volume is lowered at a constant temperature, the number of gas molecules colliding with the container's walls per unit time increases.
- The momentum transferred per unit time per unit area, i.e. the force exerted by the gas on the walls, increases as a result.
- As a result, the gas pressure rises.
उत्तर २
Let P - be the pressure exerted by the gas
V - be the volume of the gas
N - be the number of molecule of gas
m - be the mass of each molecule of gas.
∴ Total mass of the gas, M = Nm.
From kinetic theory of gases,
`P = (1/3) (Nm)/V barv^2`
∴ Pressure exerted by gas in an enclosed vessel is
`P = 2/3 N/V (1/2mbarv^2)`
But `1/2mbarv^2` = (Kinetic energy at constant temperature)
N is number which is also constant.
∴ `P = "Constant"/V`
∴ `P ∝ 1/V`
As a result, at constant temperature, increasing the pressure of the gas reduces its volume.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
A gas is kept in an enclosure. The pressure of the gas is reduced by pumping out some gas. Will the temperature of the gas decrease by Charles's low?
If the molecules were not allowed to collide among themselves, would you expect more evaporation or less evaporation?
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
Air is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw at a pressure of 2 atm. The volume of each tube at this pressure is 0.002 m3. One of the tubes gets punctured and the volume of the tube reduces to 0.0005 m3. How many moles of air have leaked out? Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300 K and that the air behaves as an ideal gas.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
0.040 g of He is kept in a closed container initially at 100.0°C. The container is now heated. Neglecting the expansion of the container, calculate the temperature at which the internal energy is increased by 12 J.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 10 cm2 and weight 1 kg in figure. The vessel itself is kept in a big chamber containing air at atmospheric pressure 100 kPa. The length of the gas column is 20 cm. If the chamber is now completely evacuated by an exhaust pump, what will be the length of the gas column? Assume the temperature to remain constant throughout the process.
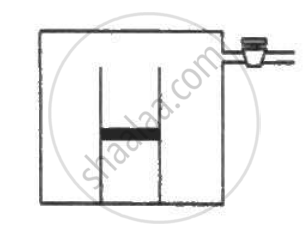
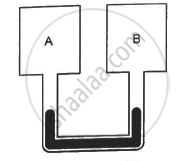
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9 × 10 6 ms−1 and 1 × 106 ms−1, respectively. What is the root mean square speed of these molecules?
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
For a particle moving in vertical circle, the total energy at different positions along the path ______.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
