Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Solution 1
- At constant temperature, a gas's average kinetic energy per molecule remains constant.
- When a gas's volume is lowered at a constant temperature, the number of gas molecules colliding with the container's walls per unit time increases.
- The momentum transferred per unit time per unit area, i.e. the force exerted by the gas on the walls, increases as a result.
- As a result, the gas pressure rises.
Solution 2
Let P - be the pressure exerted by the gas
V - be the volume of the gas
N - be the number of molecule of gas
m - be the mass of each molecule of gas.
∴ Total mass of the gas, M = Nm.
From kinetic theory of gases,
`P = (1/3) (Nm)/V barv^2`
∴ Pressure exerted by gas in an enclosed vessel is
`P = 2/3 N/V (1/2mbarv^2)`
But `1/2mbarv^2` = (Kinetic energy at constant temperature)
N is number which is also constant.
∴ `P = "Constant"/V`
∴ `P ∝ 1/V`
As a result, at constant temperature, increasing the pressure of the gas reduces its volume.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
Find the number of molecules of an ideal gas in a volume of 1.000 cm3 at STP.
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
An adiabatic cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area 1 cm2 is closed at one end and fitted with a piston at the other end. The tube contains 0.03 g of an ideal gas. At 1 atm pressure and at the temperature of the surrounding, the length of the gas column is 40 cm. The piston is suddenly pulled out to double the length of the column. The pressure of the gas falls to 0.355 atm. Find the speed of sound in the gas at atmospheric temperature.
Answer in brief:
Show that rms velocity of an oxygen molecule is `sqrt2` times that of a sulfur dioxide molecule at S.T.P.
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
Earth’s mean temperature can be assumed to be 280 K. How will the curve of blackbody radiation look like for this temperature? Find out λmax. In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum, does this value lie? (Take Wien's constant b = 2.897 × 10−3 m K)
The number of degrees of freedom, for the vibrational motion of a polyatomic molecule, depends on the ______
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
Under which condition laws of Boyle, Charles, and Gay-Lussac are valid?
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
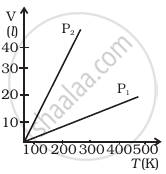
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of average K.E.
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
For a particle moving in vertical circle, the total energy at different positions along the path ______.
At what temperature will therms velocity of a gas be four times its value at STP?
2000 calories of radiant heat is incident on a body. If the body absorbs 550 calories of heat, find the coefficient of emmission of the body.
