Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An adiabatic cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area 1 cm2 is closed at one end and fitted with a piston at the other end. The tube contains 0.03 g of an ideal gas. At 1 atm pressure and at the temperature of the surrounding, the length of the gas column is 40 cm. The piston is suddenly pulled out to double the length of the column. The pressure of the gas falls to 0.355 atm. Find the speed of sound in the gas at atmospheric temperature.
Solution
Given:
Area of the tube, A = 1 cm2 = 1 × 10−4 m2
Mass of the gas, M = 0.03 g = 0.03 × 10−3 kg
Initial pressure, P = 1 atm = 105 Pascal
Initial length of the mercury column, L = 40 cm = 0.4 m
Final length of the mercury column, L1 = 80 cm = 0.8 m
Final pressure, P' = 0.355 atm
The process is adiabatic. So,
P(V)γ = P'(V')γ
⇒ 1 × (A × 0.4)γ = 0.355 × (A × 0.8)γ
⇒ 1 × 1 = 0.355 × 2γ
`=> 1/0.355 = 2^gamma`
`gamma "log" 2 = "log"(1/0.355)`
⇒ γ =1.4941
Speed of sound in the gas,
`"v" = sqrt((gamma"P")/ρ) = sqrt ((gamma"P")/("m"/"v"))`
`"v" = sqrt ((1.4941 xx 10^5)/("m"/"v")) = sqrt ((1.4941 xx 10^5)/(( 0.03 xx 10 ^-3)/(10 ^-4 xx 1 xx 0.4)`
⇒ v = 446.33 ≈ 447 m/s
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Consider a gas of neutrons. Do you expect it to behave much better as an ideal gas as compared to hydrogen gas at the same pressure and temperature?
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
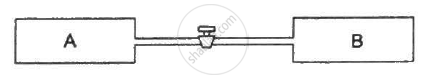
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
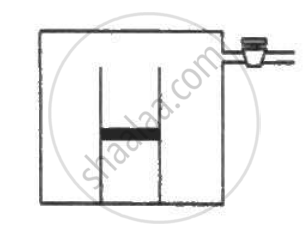
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 10 cm2 and weight 1 kg in figure. The vessel itself is kept in a big chamber containing air at atmospheric pressure 100 kPa. The length of the gas column is 20 cm. If the chamber is now completely evacuated by an exhaust pump, what will be the length of the gas column? Assume the temperature to remain constant throughout the process.
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
Answer in brief:
Compare the rms speed of hydrogen molecules at 127ºC with rms speed of oxygen molecules at 27ºC given that molecular masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 2 and 32 respectively.
In an ideal gas, the molecules possess
If the density of oxygen is 1.44 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 N/m2, find the root mean square velocity of oxygen molecules.
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
Find the temperature of a blackbody if its spectrum has a peak at (a) λmax = 700 nm (visible), (b) λmax = 3 cm (microwave region) (c) λmax = 3 m (short radio waves). (Take Wien’s constant b = 2.897 × 10-3 m.K).
The number of degrees of freedom, for the vibrational motion of a polyatomic molecule, depends on the ______
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
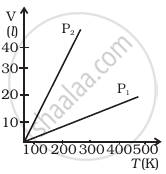
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of average K.E.
The Q-value of a nuclear reaction and kinetic energy of the projectile particle, KP are related as ______.
If a = 0. 72 and t = 0.04, then the value of r is ______.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
