Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
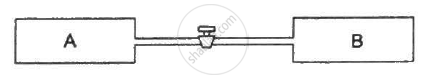
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
Solution
Let the partial pressure of the gas in chamber A and B be P'A and P'B , respectively.
Applying equation of state for gas A, we get
`{P_A V}/{T_A} = (P'_A2V)/T`
`rArr P'_A=(P_AT)/(2T_A)`
Similarly, For gas B :
`P'_B = (P_BT)/(2T_B)`
Total Pressure is the sum of the partial pressures . It is given by
P = P'A + P'B
= `(P_AT)/(2T_A) + (P_BT)/(2T_B)`
⇒ P = `T/2(P_A/T_A + P_B/T_B)`
⇒ `P/T` = `1/2 (P_A/T_A + P_B/T_B)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
The average translational kinetic energy of air molecules is 0.040 eV (1 eV = 1.6 × 10−19J). Calculate the temperature of the air. Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1.
Air is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw at a pressure of 2 atm. The volume of each tube at this pressure is 0.002 m3. One of the tubes gets punctured and the volume of the tube reduces to 0.0005 m3. How many moles of air have leaked out? Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300 K and that the air behaves as an ideal gas.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
An ideal gas is trapped between a mercury column and the closed-end of a narrow vertical tube of uniform base containing the column. The upper end of the tube is open to the atmosphere. The atmospheric pressure equals 76 cm of mercury. The lengths of the mercury column and the trapped air column are 20 cm and 43 cm respectively. What will be the length of the air column when the tube is tilted slowly in a vertical plane through an angle of 60°? Assume the temperature to remain constant.
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area A fitted with two frictionless pistons. The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire. Initially, the temperature of the gas is T0 and its pressure is p0 which equals the atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the tension in the wire? (b) What will be the tension if the temperature is increased to 2T0 ?

The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

An adiabatic cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area 1 cm2 is closed at one end and fitted with a piston at the other end. The tube contains 0.03 g of an ideal gas. At 1 atm pressure and at the temperature of the surrounding, the length of the gas column is 40 cm. The piston is suddenly pulled out to double the length of the column. The pressure of the gas falls to 0.355 atm. Find the speed of sound in the gas at atmospheric temperature.
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
In an ideal gas, the molecules possess
Find the kinetic energy of 5 litres of a gas at STP, given the standard pressure is 1.013 × 105 N/m2.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
When photons of energy hv fall on a metal plate of work function 'W0', photoelectrons of maximum kinetic energy 'K' are ejected. If the frequency of the radiation is doubled, the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected photoelectrons will be ______.
Assuming the expression for the pressure exerted by the gas on the wall of the container, it can be shown that pressure is ______.
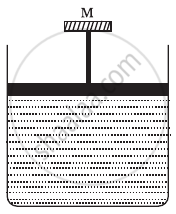
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
According to the kinetic theory of gases, at a given temperature, molecules of all gases have the same ______.
If a = 0. 72 and t = 0.04, then the value of r is ______.
