Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
Solution
Yes, at equilibrium all the molecules in a sample of gas have the same temperature. This is because temperature is defined as the average kinetic energy for all the molecules in a system. Since all the molecules have the same average, temperature will be the same for all the molecules.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
If the molecules were not allowed to collide among themselves, would you expect more evaporation or less evaporation?
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
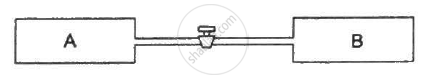
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process `P = (P_0)/(1+(V/V_0)^2` where `p_0` and `V_0` are constants . Find the temperature of the gas when `V=V_0` .
Answer in brief:
A gas in a cylinder is at pressure P. If the masses of all the molecules are made one-third of their original value and their speeds are doubled, then find the resultant pressure.
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
What is the microscopic origin of temperature?
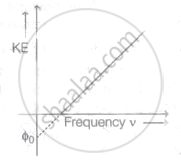
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
A ring of mass m and radius r rotates about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with angular velocity `omega`. Its kinetic energy is ______.
Explain why there is no atmosphere on moon.
