Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
Solution
A gas's molecules are in a state of constant random motion. They possess kinetic energy. When a gas is heated, the average kinetic energy per molecule of the gas increases. As a result, its temperature rises (the average kinetic energy per molecule being proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When we place a gas cylinder on a van and the van moves, does the kinetic energy of the molecules increase? Does the temperature increase?
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
Consider a gas of neutrons. Do you expect it to behave much better as an ideal gas as compared to hydrogen gas at the same pressure and temperature?
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
Air is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw at a pressure of 2 atm. The volume of each tube at this pressure is 0.002 m3. One of the tubes gets punctured and the volume of the tube reduces to 0.0005 m3. How many moles of air have leaked out? Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300 K and that the air behaves as an ideal gas.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
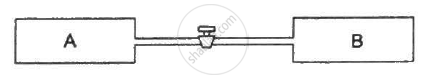
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
A metal cube of length 4 cm radiates heat at the rate of 10 J/s. Find its emissive power at a given temperature.
The average translational kinetic energy of gas molecules depends on ____________.
What is the microscopic origin of temperature?
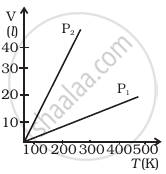
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
Explain why there is no atmosphere on moon.
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
A proton, a deuteron and an α-particle with same kinetic energy enter into a uniform magnetic field at right angle to magnetic field. The ratio of the radii of their respective circular paths is ______.
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
At what temperature will therms velocity of a gas be four times its value at STP?
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
