Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
Solution
(a) Temperature is defined as the average kinetic energy of he partciles. In a vacuum, devoid of any electromagnetic fields and molecules or entities, the temperature cannot be defined as there are no molecules or atoms or entities.
(b) No, we cannot define temperature of a single molecule. Since temperature is defined as the average kinetic energy of the particles, it is defined only statistically for a large collection of molecules.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Find the kinetic energy of 5 litres of a gas at STP, given the standard pressure is 1.013 × 105 N/m2.
Find the temperature of a blackbody if its spectrum has a peak at (a) λmax = 700 nm (visible), (b) λmax = 3 cm (microwave region) (c) λmax = 3 m (short radio waves). (Take Wien’s constant b = 2.897 × 10-3 m.K).
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
On what, the values of absorption coefficient, reflection coefficient, and transmission coefficient depend, in addition to the material of the object on which the radiation is an incident?
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
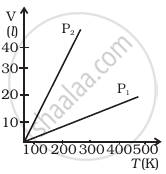
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of average K.E.
Explain why there is no atmosphere on moon.
23Ne decays to 23Na by negative beta emission. Mass of 23Ne is 22.994465 amu mass of 23Na is 22.989768 amu. The maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons neglecting the kinetic energy of recoiling product nucleus is ______ MeV.
A proton, a deuteron and an α-particle with same kinetic energy enter into a uniform magnetic field at right angle to magnetic field. The ratio of the radii of their respective circular paths is ______.
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
At what temperature will therms velocity of a gas be four times its value at STP?
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
