Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

Solution
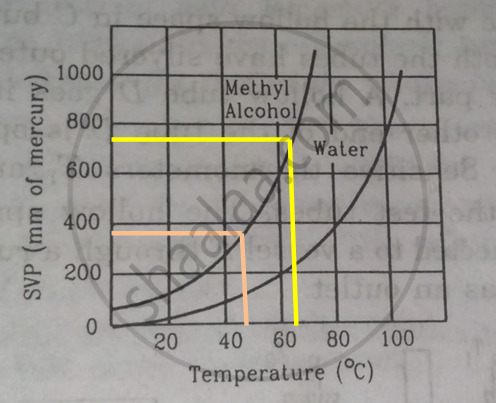
We drop a perpendicular on x-axis corresponding to the saturated vapour pressure 760 mm. This gives the boiling point 650 of methyl alcohol.
For 0.5 atm pressure, corresponding pressure in mm Hg will be 375 mm. We drop a perpendicular on x-axis corresponding to the saturated vapour pressure 375 mm. This gives the boiling point 480of methyl alcohol.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When we place a gas cylinder on a van and the van moves, does the kinetic energy of the molecules increase? Does the temperature increase?
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
0.040 g of He is kept in a closed container initially at 100.0°C. The container is now heated. Neglecting the expansion of the container, calculate the temperature at which the internal energy is increased by 12 J.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
An ideal gas is trapped between a mercury column and the closed-end of a narrow vertical tube of uniform base containing the column. The upper end of the tube is open to the atmosphere. The atmospheric pressure equals 76 cm of mercury. The lengths of the mercury column and the trapped air column are 20 cm and 43 cm respectively. What will be the length of the air column when the tube is tilted slowly in a vertical plane through an angle of 60°? Assume the temperature to remain constant.
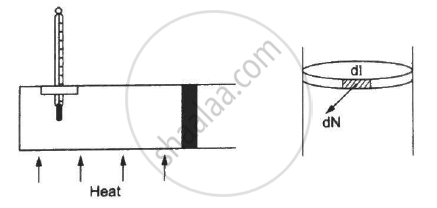
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
A glass contains some water at room temperature 20°C. Refrigerated water is added to it slowly. when the temperature of the glass reaches 10°C, small droplets condense on the outer surface. Calculate the relative humidity in the room. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 17.5 mm of mercury is 20°C and at 8.9 mm of mercury it is 10°C.
Answer in brief:
What will happen to the mean square speed of the molecules of a gas if the temperature of the gas increases?
Answer in brief:
A gas in a cylinder is at pressure P. If the masses of all the molecules are made one-third of their original value and their speeds are doubled, then find the resultant pressure.
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Energy is emitted from a hole in an electric furnace at the rate of 20 W when the temperature of the furnace is 727°C. What is the area of the hole? (Take Stefan’s constant σ to be 5.7 × 10-8 Js-1 m-2K-4.)
The emissive power of a sphere of area 0.02 m2 is 0.5 kcal s-1m-2. What is the amount of heat radiated by the spherical surface in 20 seconds?
Find the temperature of a blackbody if its spectrum has a peak at (a) λmax = 700 nm (visible), (b) λmax = 3 cm (microwave region) (c) λmax = 3 m (short radio waves). (Take Wien’s constant b = 2.897 × 10-3 m.K).
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
Above what temperature, all bodies radiate electromagnetic radiation?
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
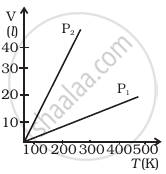
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9 × 10 6 ms−1 and 1 × 106 ms−1, respectively. What is the root mean square speed of these molecules?
An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity vo. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
