Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An ideal gas is trapped between a mercury column and the closed-end of a narrow vertical tube of uniform base containing the column. The upper end of the tube is open to the atmosphere. The atmospheric pressure equals 76 cm of mercury. The lengths of the mercury column and the trapped air column are 20 cm and 43 cm respectively. What will be the length of the air column when the tube is tilted slowly in a vertical plane through an angle of 60°? Assume the temperature to remain constant.
Solution
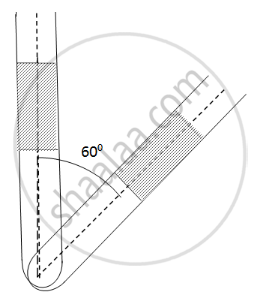
Here ,
Initial pressure = Atmospheric pressure + pressure due to mercury
⇒ P1 = P0 + PHg
Let the CSA of the tube be A.
P1 = 0.76 + 0.2 = 0.96 m Hg
T1 = T2 = T
V1 = 0.43 A
If the tube is slanted , then the atmospheric pressure P0 remains the same . only the PHg changes
`P_2 = P_0 + P_Hg cos60^circ` = 0.76 + 0.2 × 0.5 = 0.86
`P_1V_1 = P_2V_2`
⇒ `V_2 = (P_1V_1)/P_2 = (0.96×0.43A)/0.86`
Let the length of the air column be l.
⇒ Al = `(P_1V_1)/P_2 = (0.96×0.43A)/0.86`
⇒ l = 0.48 m
⇒ l = 48 cm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
Consider a gas of neutrons. Do you expect it to behave much better as an ideal gas as compared to hydrogen gas at the same pressure and temperature?
A gas is kept in an enclosure. The pressure of the gas is reduced by pumping out some gas. Will the temperature of the gas decrease by Charles's low?
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area A fitted with two frictionless pistons. The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire. Initially, the temperature of the gas is T0 and its pressure is p0 which equals the atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the tension in the wire? (b) What will be the tension if the temperature is increased to 2T0 ?

The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
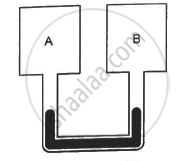
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
Answer in brief:
A gas in a cylinder is at pressure P. If the masses of all the molecules are made one-third of their original value and their speeds are doubled, then find the resultant pressure.
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas is 'E1'. The kinetic energy of the electron (e) accelerated from rest through p.d. 'V' volt is 'E2'. The temperature at which E1 = E2 is possible, is ______.
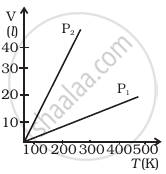
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9 × 10 6 ms−1 and 1 × 106 ms−1, respectively. What is the root mean square speed of these molecules?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
A proton, a deuteron and an α-particle with same kinetic energy enter into a uniform magnetic field at right angle to magnetic field. The ratio of the radii of their respective circular paths is ______.
