Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The emissive power of a sphere of area 0.02 m2 is 0.5 kcal s-1m-2. What is the amount of heat radiated by the spherical surface in 20 seconds?
Solution
Data: R = 0.5 kcal s-1m-2, A = 0.02 m2, t = 20 s
Q = RAt = (0.5)(0.02)(20) = 0.2 kcal
This is the required quantity.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process `P = (P_0)/(1+(V/V_0)^2` where `p_0` and `V_0` are constants . Find the temperature of the gas when `V=V_0` .
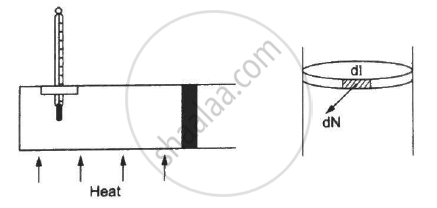
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
Answer in brief:
Show that rms velocity of an oxygen molecule is `sqrt2` times that of a sulfur dioxide molecule at S.T.P.
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Answer in brief:
Compare the rms speed of hydrogen molecules at 127ºC with rms speed of oxygen molecules at 27ºC given that molecular masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 2 and 32 respectively.
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Find the kinetic energy of 5 litres of a gas at STP, given the standard pressure is 1.013 × 105 N/m2.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
Energy is emitted from a hole in an electric furnace at the rate of 20 W when the temperature of the furnace is 727°C. What is the area of the hole? (Take Stefan’s constant σ to be 5.7 × 10-8 Js-1 m-2K-4.)
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
A metal cube of length 4 cm radiates heat at the rate of 10 J/s. Find its emissive power at a given temperature.
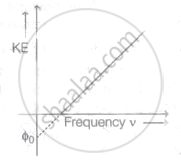
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
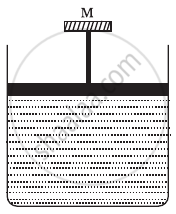
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
The Q-value of a nuclear reaction and kinetic energy of the projectile particle, KP are related as ______.
A proton, a deuteron and an α-particle with same kinetic energy enter into a uniform magnetic field at right angle to magnetic field. The ratio of the radii of their respective circular paths is ______.
At what temperature will therms velocity of a gas be four times its value at STP?
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
2000 calories of radiant heat is incident on a body. If the body absorbs 550 calories of heat, find the coefficient of emmission of the body.
