Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The emissive power of a sphere of area 0.02 m2 is 0.5 kcal s-1m-2. What is the amount of heat radiated by the spherical surface in 20 seconds?
उत्तर
Data: R = 0.5 kcal s-1m-2, A = 0.02 m2, t = 20 s
Q = RAt = (0.5)(0.02)(20) = 0.2 kcal
This is the required quantity.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
Consider a gas of neutrons. Do you expect it to behave much better as an ideal gas as compared to hydrogen gas at the same pressure and temperature?
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
The average translational kinetic energy of air molecules is 0.040 eV (1 eV = 1.6 × 10−19J). Calculate the temperature of the air. Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1.
Air is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw at a pressure of 2 atm. The volume of each tube at this pressure is 0.002 m3. One of the tubes gets punctured and the volume of the tube reduces to 0.0005 m3. How many moles of air have leaked out? Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300 K and that the air behaves as an ideal gas.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey an additional law pV2 = constant. The gas is initially at a temperature T and volume V. Find the temperature when it expands to a volume 2V.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

Answer in brief:
Show that rms velocity of an oxygen molecule is `sqrt2` times that of a sulfur dioxide molecule at S.T.P.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
Above what temperature, all bodies radiate electromagnetic radiation?
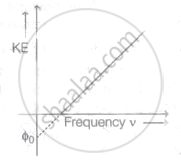
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
A ring of mass m and radius r rotates about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with angular velocity `omega`. Its kinetic energy is ______.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
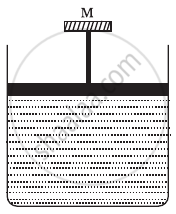
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of average K.E.
The Q-value of a nuclear reaction and kinetic energy of the projectile particle, KP are related as ______.
For a particle moving in vertical circle, the total energy at different positions along the path ______.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
