Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
उत्तर
Data: T = 273 + 127 = 400 K,
molecular weight = 32
∴ molar mass = 32 kg/kmol,
R = 8.31 Jmol-1K-1,
NA = 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol-1
(i) The average molecular kinetic energy per kmol of oxygen = the average kinetic energy per mol of oxygen × 1000
`= 3/2 "RT" xx 1000`
= `3/2(8.31)(400)(10^3)"J"/"kmol"`
= (600)(8.31)(103)
= 4.986 × 106 J/kmol
(ii) The average molecular kinetic energy per kg of oxygen
= `3/2 "RT"/"M"_0`
= `(4.986xx10^6 "J"//"mol")/(32 "kg"//"kmol")`
= 1.558 × 105 J/kg.
(iii) The average molecular kinetic energy per molecule of oxygen
= `3/2 "RT"/"N"_"A"`
= `(4.986 xx 10^6 "J"//"mol")/(6.02 xx 10^23 "molecule"//"mol")`
= 8.282 × 10-21 J/molecule
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
Consider a gas of neutrons. Do you expect it to behave much better as an ideal gas as compared to hydrogen gas at the same pressure and temperature?
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
Find the number of molecules of an ideal gas in a volume of 1.000 cm3 at STP.
A gas cylinder has walls that can bear a maximum pressure of 1.0 × 106 Pa. It contains a gas at 8.0 × 105 Pa and 300 K. The cylinder is steadily heated. Neglecting any change in the volume, calculate the temperature at which the cylinder will break.
An ideal gas is trapped between a mercury column and the closed-end of a narrow vertical tube of uniform base containing the column. The upper end of the tube is open to the atmosphere. The atmospheric pressure equals 76 cm of mercury. The lengths of the mercury column and the trapped air column are 20 cm and 43 cm respectively. What will be the length of the air column when the tube is tilted slowly in a vertical plane through an angle of 60°? Assume the temperature to remain constant.
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

A glass contains some water at room temperature 20°C. Refrigerated water is added to it slowly. when the temperature of the glass reaches 10°C, small droplets condense on the outer surface. Calculate the relative humidity in the room. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 17.5 mm of mercury is 20°C and at 8.9 mm of mercury it is 10°C.
Answer in brief:
What will happen to the mean square speed of the molecules of a gas if the temperature of the gas increases?
Answer in brief:
A gas in a cylinder is at pressure P. If the masses of all the molecules are made one-third of their original value and their speeds are doubled, then find the resultant pressure.
In an ideal gas, the molecules possess
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
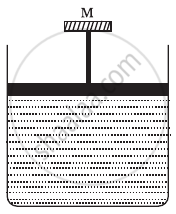
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9 × 10 6 ms−1 and 1 × 106 ms−1, respectively. What is the root mean square speed of these molecules?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
For a particle moving in vertical circle, the total energy at different positions along the path ______.
Assuming the expression for the pressure P exerted by an ideal gas, prove that the kinetic energy per unit volume of the gas is `3/2` P.
