Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A glass contains some water at room temperature 20°C. Refrigerated water is added to it slowly. when the temperature of the glass reaches 10°C, small droplets condense on the outer surface. Calculate the relative humidity in the room. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 17.5 mm of mercury is 20°C and at 8.9 mm of mercury it is 10°C.
उत्तर
Here ,
Dew point = `10^circ` C [∵ Dew appears at `10^circ`C]
At boiling point, SVP equals atmospheric pressure.
At `20^circ` C , SVP = 17.5 mmHg
At dew point , SVP = 8.9 mmHg
`"RH" = ("SVP at dew point") /("SVP at air temperature") xx 100%`
= `8.9/17.5 xx 100%`
= 51%
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When we place a gas cylinder on a van and the van moves, does the kinetic energy of the molecules increase? Does the temperature increase?
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
Air is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw at a pressure of 2 atm. The volume of each tube at this pressure is 0.002 m3. One of the tubes gets punctured and the volume of the tube reduces to 0.0005 m3. How many moles of air have leaked out? Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300 K and that the air behaves as an ideal gas.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process `P = (P_0)/(1+(V/V_0)^2` where `p_0` and `V_0` are constants . Find the temperature of the gas when `V=V_0` .
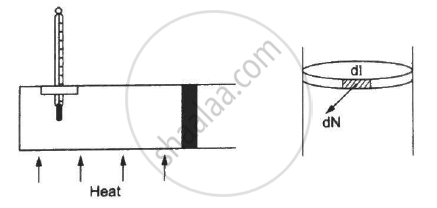
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
Answer in brief:
A gas in a cylinder is at pressure P. If the masses of all the molecules are made one-third of their original value and their speeds are doubled, then find the resultant pressure.
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
Assuming the expression for the pressure exerted by the gas on the wall of the container, it can be shown that pressure is ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
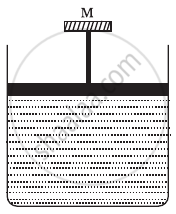
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
